Figure 4. Rosiglitazone Suppresses Several Members of the Metallothionein Gene Family.
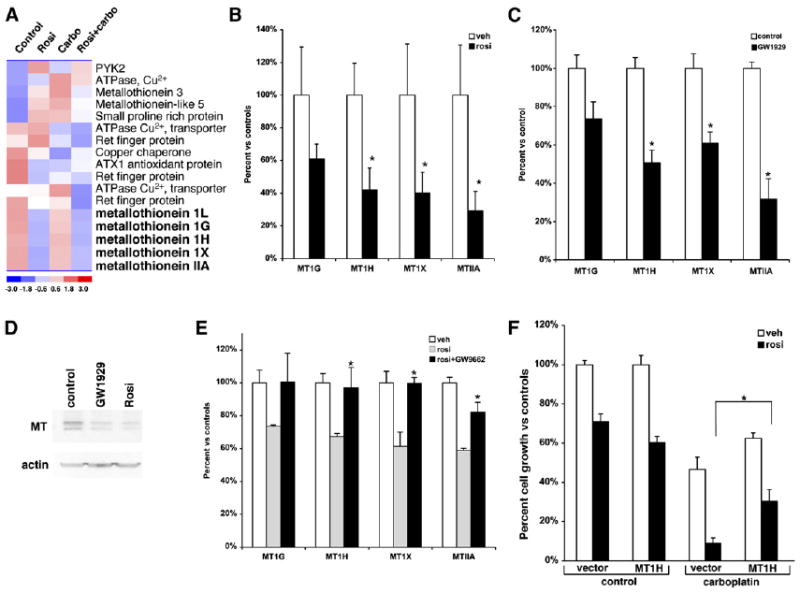
(A) Heat diagram of cluster analysis for heavy metal binding proteins from microarray data of RNA following treatment with rosiglitazone, carboplatin, or a combination of the two.
(B) Real-time PCR for the expression of metallothioneins 1G, 1H, 1X, and IIA following treatment of A549 cells with 1 μM rosiglitazone for 24 hr.
(C) Real-time PCR for the expression of metallothioneins 1G, 1H, 1X, and IIA following treatment of A549 cells with 250 nM GW1929 for 24 hr.
(D) Metallothionein protein expression in A549 cells following treatment with PPARγ agonists GW1929 (250 nM) or rosiglitazone (1 μM) for 24 hr.
(E) A549 cells were treated with 1 μM rosiglitazone alone or in combination with the PPARγ antagonist GW9662 for 24 hr, and real-time PCR was carried out for MT1G, MT1H, MT1X, and MTIIA. *p < 0.05 rosi + GW9662 versus rosiglitazone alone.
(F) Ectopic expression of MT1H blunts the synergistic effect of rosiglitazone and carboplatin. A549 cells stably transduced with a control or retrovirus expressing MT1H were treated with 0.5 μM rosiglitazone or 10 μM carboplatin alone or in combination, and the cell number was determined using a hemocytometer after 7 days. Representative experiment, n = 3 mean ± SD. *p < 0.05.
