Figure 1.
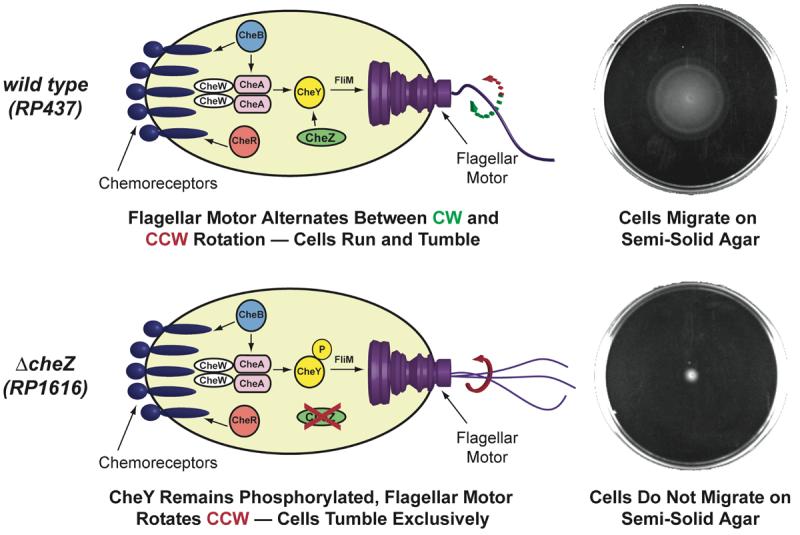
top: Proteins involved in wild-type E. coli chemotaxis. The direction of rotation of the flagellar motor is controlled by the protein CheY. When CheY is not phosphorylated, the flagellar motor rotates clockwise (CW) and the cell runs for a period of 1-3 s. When CheY is phosphorylated (CheY-P), it can bind to the flagellar motor protein FliM, causing the cell to tumble. Wild-type E. coli can migrate on semi-solid agar (top right; cells grown for 10 h at 37 °C). bottom: Cells lacking the protein CheZ (strain RP1616) cannot dephosphorylate CheY-P and these cells tumble incessantly (bottom right; cells grown for 10 h at 37 °C). Cartoon adapted from reference (34).
