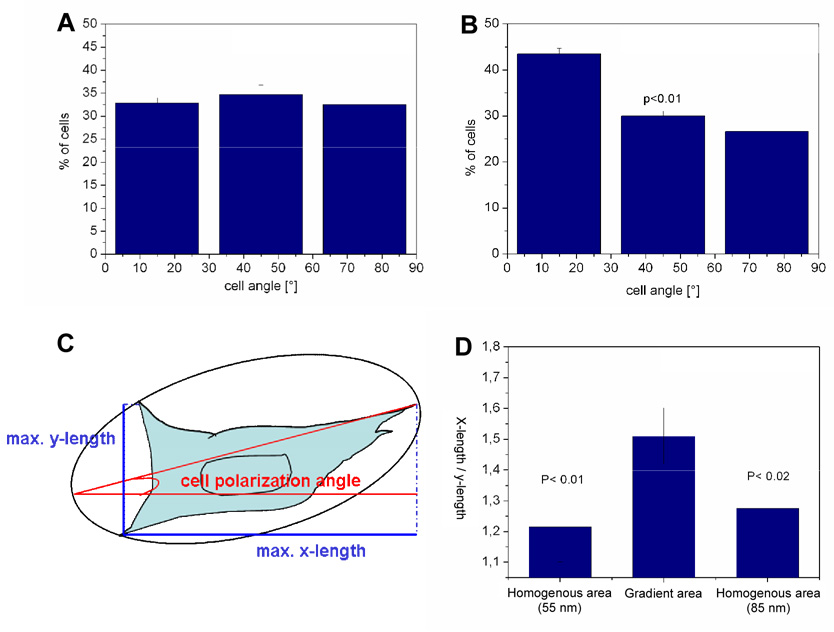
Fig. 4.
Cell polarisation along c(-RGDfK-) patch spacing gradients. Angles of the main cell body axis with the gradient direction after 23 h on 55 nm homogenously nanopatterned samples (A) and on the c(-RGDfK-) patch spacing gradient ranging from 50 to 80 nm spacing along a 2 mm substrate length (B). Data were acquired from three separate experiments. For graph (A) 347 cells and graph (B) 428 cells were evaluated, error bars present standard error, p<0.01. (C) Describes the analysis of the main cell body angle with the direction of the gradient and the gradient polarisation ratio (GPR). The GPR is given by the ratio of the maximum x-width (length parallel to the gradient axis) with the maximum y-width (length perpendicular to the gradient axis) of a cell body. GPR of a cell adhering on homogeneously nanopatterned areas (50 nm, 80 nm) and on the c(-RGDfK-) patch spacing gradient area with spacing ranging from 50 to 80 nm along 2 mm substrate length after 23 h are given in (D).