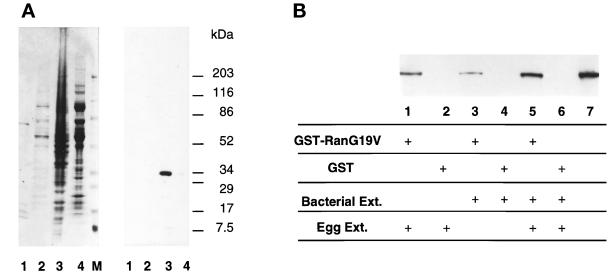
Figure 2.
Xenopus RanBP1 is a soluble Ran-binding protein. (A) RanBP1 is found in the cytosolic fraction of reconstituted extracts. Amounts of sperm chromatin, membranes, and cytosol equivalent to those in 1 μl of reconstituted extract were separated on SDS-PAGE followed by blotting to a PVDF membrane filter (lane 1, 1000 sperm nuclei; lane 2, 0.1 μl of membranes; lane 3, 0.9 μl of cytosol). Lane 4 contains 1.0 μl of the membrane fraction. The filter was stained with India ink (left lanes) followed by Western blotting with anti-Xenopus RanBP1 antibodies (right lanes). M represents protein molecular size standards in kilodaltons. (B) Xenopus RanBP1 binds GST-RanG19V. Egg cytosol (lanes 1 and 2), extracts of bacteria expressing Xenopus RanBP1 (lanes 3 and 4), or both (lane 5 and 6) were incubated with GST-RanG19V (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or GST (lanes 2, 4, and 6). Glutathione-Sepharose was added to the incubations to remove the GST-RanG19V- and GST-associated proteins. Proteins bound to the beads were eluted with sample buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins from the gel were transferred to a PVDF membrane, and Western blotting analysis was performed with anti-human RanBP1 antibodies. (Identical results were obtained when the experiment was performed with anti-Xenopus RanBP1 antibodies; our unpublished results). Lane 7 contained 1 μl of egg cytosol. GST-RanG19V was preloaded with GTP prior to this experiment. Both wild-type and his-tagged RanBP1 proteins also bound to wild-type GST-Ran but with a lower affinity that probably reflects the fact that wild-type Ran would exist as a mixed population of GTP- and GDP-bound forms (our unpublished results).