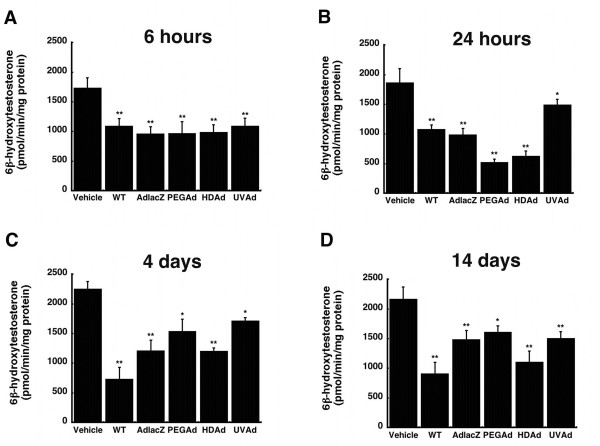
Figure 2.
Administration of a Single Dose of Active and Inactive Adenovirus Significantly Reduces Hepatic CYP3A2 Activity in the Male Sprague-Dawley Rat for 14 Days without Return to Baseline Levels. In vitro catalytic activity of CYP3A2 microsomal proteins were measured by the production of the enzyme-specific testosterone metabolite, 6β-hydroxytestosterone. Rats were treated with: phosphate buffered saline (Vehicle), wild type adenovirus serotype 5 (WT), a first generation recombinant adenovirus 5 expressing E. coli beta-galactosidase (AdlacZ), PEGylated AdlacZ, (PEGAd), helper-dependent adenovirus 5 expressing beta-galactosidase (HDAd), or inactivated AdlacZ (UVAd). Values are presented as the mean ± standard error of 4 animals/treatment/timepoint. Statistical significance was determined between individual treatment groups and saline controls by one-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni/Dunn post-hoc analysis. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.