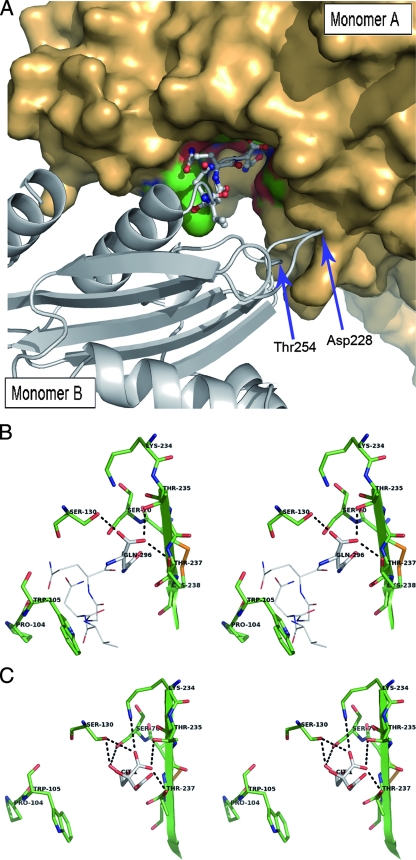
FIG. 3.
(A) View of the interactions between the crystallographically observable C-terminally extended peptide of molecule B in one asymmetric unit and the active-site cleft of molecule A from an adjacent asymmetric unit. The monomer A surface is represented in bronze, with the active-site residues colored in green and red. Monomer B is shown in a cartoon representation colored in gray, with the C-ter amino acids anchored in the active site of molecule A being represented in a ball-and-stick configuration. Asp228 and Thr254, two other residues also interacting by H-bonds with the monomer A residues Lys273 and His274, are indicated by arrows. (B) Stereo view depicting the active site of KPC-2 (monomer A, shown as green sticks) containing the last C-ter residues from a symmetric molecule (monomer B, shown with Corey-Pauling-Koltun [CPK] lines). The last residue in monomer B (Gln296) is indicated with CPK sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. (C) Stereo view showing the active site of the C-ter-deleted mutant of KPC-2 (green sticks) with a bound citrate molecule (CPK sticks).