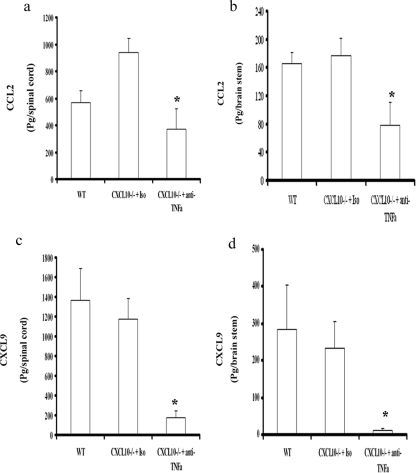
FIG. 4.
CCL2 and CXCL9 levels in the CNSs of mice. Depo-Provera-treated WT and CXCL10−/− mice (n = 12/group) were infected with HSV-2 (2,000 PFU/vagina). On day 5 postinfection, 100 μg of anti-mouse TNF-α or isotypic control Ab was administered intravenously (retro-orbitally) into HSV-2-infected CXCL10−/− mice. On day 7 postinfection, the mice were exsanguinated and the spinal cord and brain stem were removed from each mouse, processed, and analyzed for CCL2 (spinal cord) (a), CCL2 (brain stem) (b), CXCL9 (spinal cord) (c), and CXCL9 (brain stem) (d) content by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Samples were run in duplicate and analyzed along with a known standard provided for each analyte by the manufacturer, with the unknown amount extrapolated from the standard curve generated for each assay. The bars represent the means ± SEM of results from three experiments for the indicated chemokine. *, P values of <0.05 for comparison of the isotypic control Ab-treated CXCL10−/− mice to the other two groups (A) or for comparison of the anti-TNF-α Ab-treated CXCL10−/− mice to the WT mice (B), as determined by ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc t test.