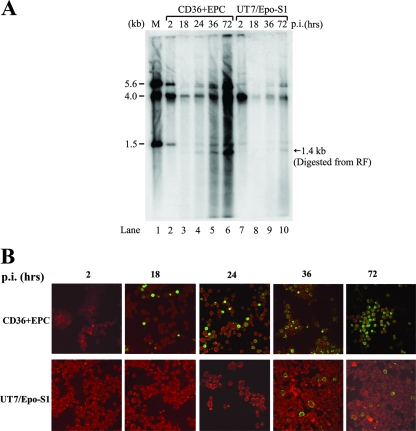
FIG. 2.
B19V infection of CD36+ EPCs and UT7/Epo-S1 cells. CD36+ EPCs or UT7/Epo-S1 cells were infected with B19V. (A) Southern blotting. Hirt DNAs were isolated at different time points p.i., as indicated at the top of the figure. BamHI-digested fragments were resolved in 1% agarose and were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The blot was hybridized with the B19V NSCap probe spanning the B19V genome at nt 199 to 5410. Lane 1 shows the BamHI-digested bands of B19V infectious DNA (nt 1 to 5596) as a control and a size marker. (B) Immunofluorescence assay. B19V-infected cells were collected at different time points p.i., as indicated at the top, and were cytocentrifuged onto slides by use of a Shandon Cytospin 3 centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, MA). Fixed cells were incubated with a mouse monoclonal antibody that reacted only with assembled B19V capsids (clone 5215D; Millipore) and were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody. The background was counterstained with Evans blue. Images were acquired by an Eclipse C1 Plus confocal microscope (Nikon) at a magnification of ×40.