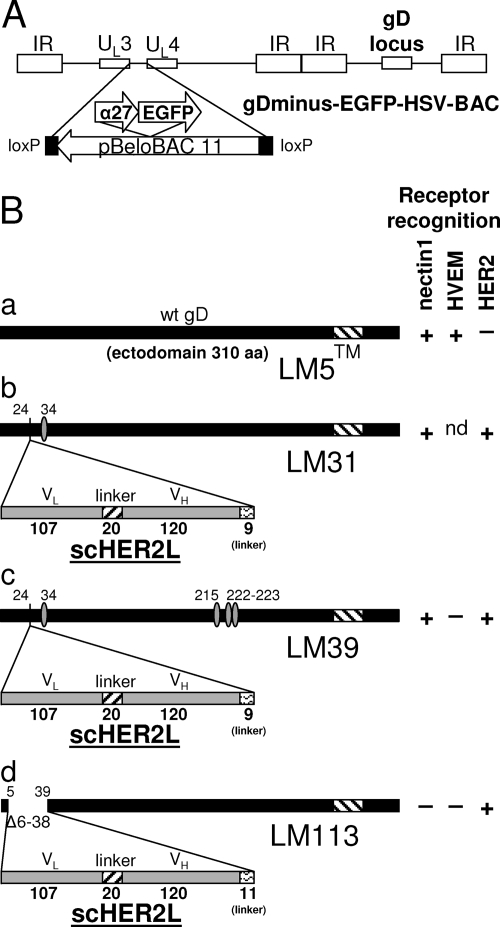
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the recombinant HSV-BACs generated in this study. The backbone of gD-minus-EGFP-HSV-BAC is shown as an example. The HSV-BACs are derived from pYEbac102 (54), which carries pBeloBAC11 sequences inserted between UL3 and UL4. In gD-minus-EGFP-HSV-BAC, the reporter cassette (α27-EGFP) is inserted in the BAC sequences. gD-minus-LacZ-HSV-BAC has the same structure but carries LacZ in place of EGFP. (B) Schematic representations of wt gD (a) and the gD-scHER2 chimeric proteins. gD of recombinant R-LM31 carries a substitution at amino acid residue 34 (b); gD of recombinant R-LM39 carries mutations at amino acid residues 34, 215, 222, and 223 (c); and gD of recombinant R-LM113 carries scHER2 in place of amino acid residues 6 to 38 (d). The boldface numbers indicate the length in amino acid residues of each fragment. The lightface numbers refer to amino acid residues according to wt gD coordinates. Mutated residues are indicated by ovals (Table 1). For each virus expressing wt or chimeric gD, the pattern of receptor recognition is summarized in the right-hand columns as +, −, or not determined (nd). TM, transmembrane domain. VH and VL, heavy- and light-chain variable domains of the anti-HER2 antibody 4D5; Δ, deletion. In panel B, the bars are drawn to scale.