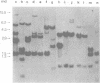
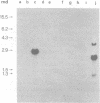
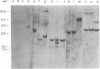
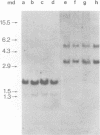
Abstract
Avian myeloblastosis virus contains a continuous sequence of approximately 1,000 nucleotides which may represent a gene (amv) responsible for acute myeloblastic leukemia in chickens. This sequence appears to have been acquired from chicken DNA and to be substituted for the envelope gene in the viral genome. We used hybridization probes enriched for the amv sequences and conditions that facilitate annealing of partially homologous nucleotide sequences to show that cellular sequences related to amv are present in the genomes of all vertebrates ranging from amphibians to humans but were not detected in fish, sea urchins, or Escherichia coli. In contrast to the preceding findings, nontransforming endogenous proviral nucleotide sequences closely related to the remainder of the avian myeloblastosis virus genome and to the entire myeloblastosis-associated helper virus are present only in chicken DNA. The amv-related cellular sequences appear to be highly conserved during evolution and to be contained at only one or a few locations in the genome of vertebrates. Within closely related species, they appear to share common evolutionary genetic loci. These findings and similar ones obtained with other highly oncogenic retroviruses containing a transforming gene suggest a general mechanism for acquisition of viral oncogenic sequences and an essential role for these sequences in the normal cellular state.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M. Endogenous viral genes of the White Leghorn chicken: common site of residence and sites associated with specific phenotypes of viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5941–5945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluda M. A., Drohan W. N. Distribution of deoxyribonucleic acid complementary to the ribonucleic acid of avian myeloblastosis virus in tissues of normal and tumor-bearing chickens. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1002–1009. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1002-1009.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluda M. A. Widespread presence, in chickens, of DNA complementary to the RNA genome of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):576–580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann D. G., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A. Characterization of avian myeloblastosis-associated virus DNA intermediates. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):366–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.366-372.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Quintrell N., Sheiness D. K., Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E. Origin and function of avian retrovirus transforming genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):919–930. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C., Andersen P. R., Dunn C. Y., Aaronson S. A. Cellular origin of the transforming gene of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):727–734. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Moscovici C. Genetic structure of avian myeloblastosis virus, released from transformed myeloblasts as a defective virus particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Das S., Neiman P., Weintraub H. Regulation of expression and chromosomal subunit conformation of avian retrovirus genomes. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):865–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Payvar F., Spector D., Schimke R. T., Robinson H. L., Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Heterogeneity of genetic loci in chickens: analysis of endogenous viral and nonviral genes by cleavage of DNA with restriction endonucleases. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Shank P. R., Spector D. H., Kung H. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Breitman M. L. Proviruses of avian sarcoma virus are terminally redundant, co-extensive with unintegrated linear DNA and integrated at many sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1397–1410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Kee S. G., Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C. Amplification and characterization of a beta-globin gene synthesized in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):163–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett T. G., Stubbledield E., Varmus H. E. Chicken macrochromosomes contain an endogenous provirus and microchromosomes contain sequences related to the transforming gene of ASV. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bishop J. M. DNA and RNA from uninfected vertebrate cells contain nucleotide sequences related to the putative transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.514-521.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Baluda M. A. Homology between avian oncornavirus RNAs and DNA from several avian species. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1492–1502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1492-1502.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Baluda M. A. Identification of the avian myeloblastosis virus genome. I. Identification of restriction endonuclease fragments associated with acute myeloblastic leukemia. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):317–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.317-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Briskin M. J., Hillyard R. L., Baluda M. A. Identification of the avian myeloblastosis virus genome. II. Restriction endonuclease analysis of DNA from lambda proviral recombinants and leukemic myeoblast clones. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.325-336.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Komaromy M. C., Baluda M. A. Identification of a proviral genome associated with avian myeloblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Strommer J. N., Hillyard R. L., Komaromy M. C., Baluda M. A. Cellular sequences are present in the presumptive avian myeloblastosis virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequences related to the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus are present in DNA of uninfected vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4102–4106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stéhelin D., Saule S., Roussel M., Sergeant A., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Raes M. B. Three new types of viral oncogenes in defective avian leukemia viruses. I. Specific nucleotide sequences of cellular origin correlate with specific transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1215–1223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]