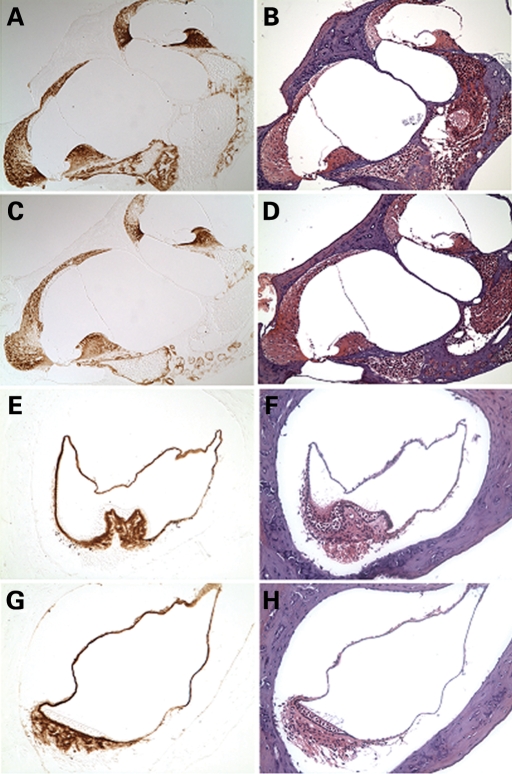
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemistry on postnatal (3-month-old) CochG88E/G88E (C, G) and Coch+/+ (A, E) mouse cochlea (A, C ×150) and crista of the posterior ampulla in the vestibular system (E, G ×200) with anti-cochlin. Immunostaining (in the left panels) appears as a reddish brown DAB reaction product; no counterstain was applied on these sections. Serial sections stained with H&E are shown in parallel in the right panels. The CochG88E/G88E mice contain only mutant Coch, therefore all immunostaining represents mutant cochlin, confirming successful translation of the mutant cochlin protein. The pattern of immunostaining in the CochG88E/G88E inner ear is similar to that of the Coch+/+ mice, as previously described (4). Prominent cochlin immunostaining is present in the fibrocytes and in the extracellular matrix throughout the spiral ligament [filled arrows in (A)] and spiral limbus [open arrow in (A)] and in the fibrocytes and stroma underlying the sensory epithelium in the crista [open arrow in (E)], as well as in the ampullary wall [filled arrow in (E)].