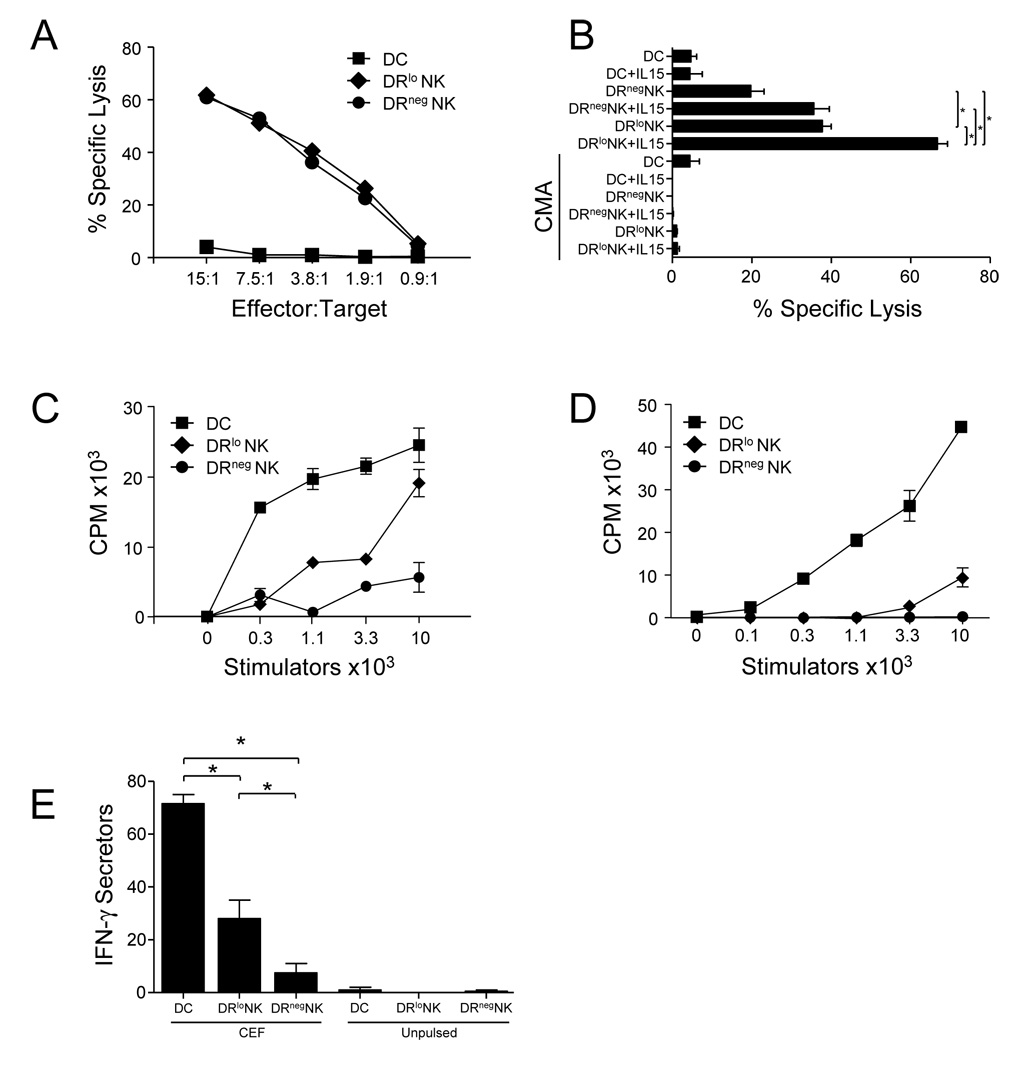
Figure 3. Freshly isolated DRlo NK cells are potent killers with weak APC function.
DC and NK cell subsets were sort-purified from PBMC of healthy donors. (A) The lytic ability of conventional (CD56−) blood DC, DRlo NK cells, and DRneg NK cells was compared in standard chromium-release lysis assays using NK cell-sensitive K562 targets. (B) Additional lysis assays were performed using NK cell resistant Daudi targets in the presence or absence of IL-15 and/or concanamycin-A. An effector:target ratio of 30:1 is shown. These data are representative of separate experiments with similar results from 4 independent donors. The relative ability of (CD56−) DC, DRlo NK cells, and DRneg NK cells isolated from blood (C) or liver (D) to stimulate the proliferation of allogeneic T cells was tested in an MLR. These data are representative of separate experiments with similar results from 4 independent donors. (E) Induction of IFN-γ production by antigen-specific memory T cells was determined by ELISPOT. Effector cells were coated with the CEF peptide pool (32 HLA Class I restricted peptides from Cytomegalovirus, Ebstein-bar virus, and Influenza virus with specificities for 15 HLA Class I alleles), washed, and then co-cultured with autologous CD8 T cells. Additional controls included peptide-pulsed and unpulsed effectors alone which produced <3 spots per group. Representative of 3 independent donors. *, p<0.05.