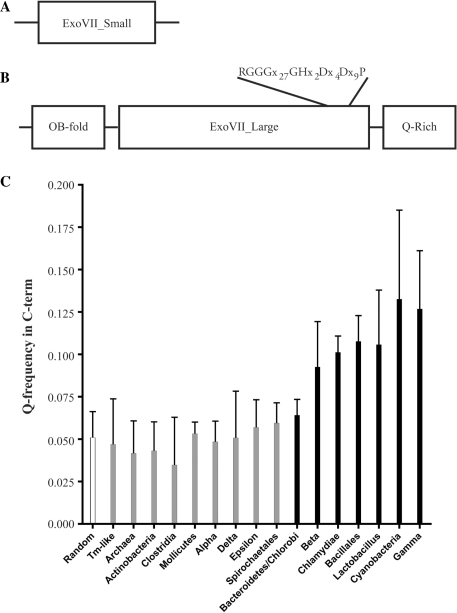
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of the ExoVII subunits. (A) Domain structure of the small subunit of ExoVII. Analysis shows that XseB homologs look like other XseB homologs with few defining motifs. (B) Domain structure of the large subunit of ExoVII. XseA has two well-defined domains (N-terminal OB-fold and central ExoVII_Large domain which contains a highly conserved core) and a putative C-terminal region which is highly enriched for glutamine residues. (C) A comparison of the frequency of glutamine occurrence in the CTD domain of XseA from a representative set of bacteria. The Q-rich CTD domain is only present (striped bars) in a subset of bacteria including Bacteroidetes, Chlamydiae, Cyanobacteria, Bacillales, Lactobacillus and β- and γ-Proteobacteria but is absent (gray bars) in Actinobacteria, Clostridia, Mollicutes, α-, δ- and ε-Proteobacteria, Spirochaetales and Archaea. Interestingly, the Q-rich CTD domain is present in E. coli but absent in T. maritima.