Figure 2. Effect of calcium and calmodulin on myo1cIQ1-3.
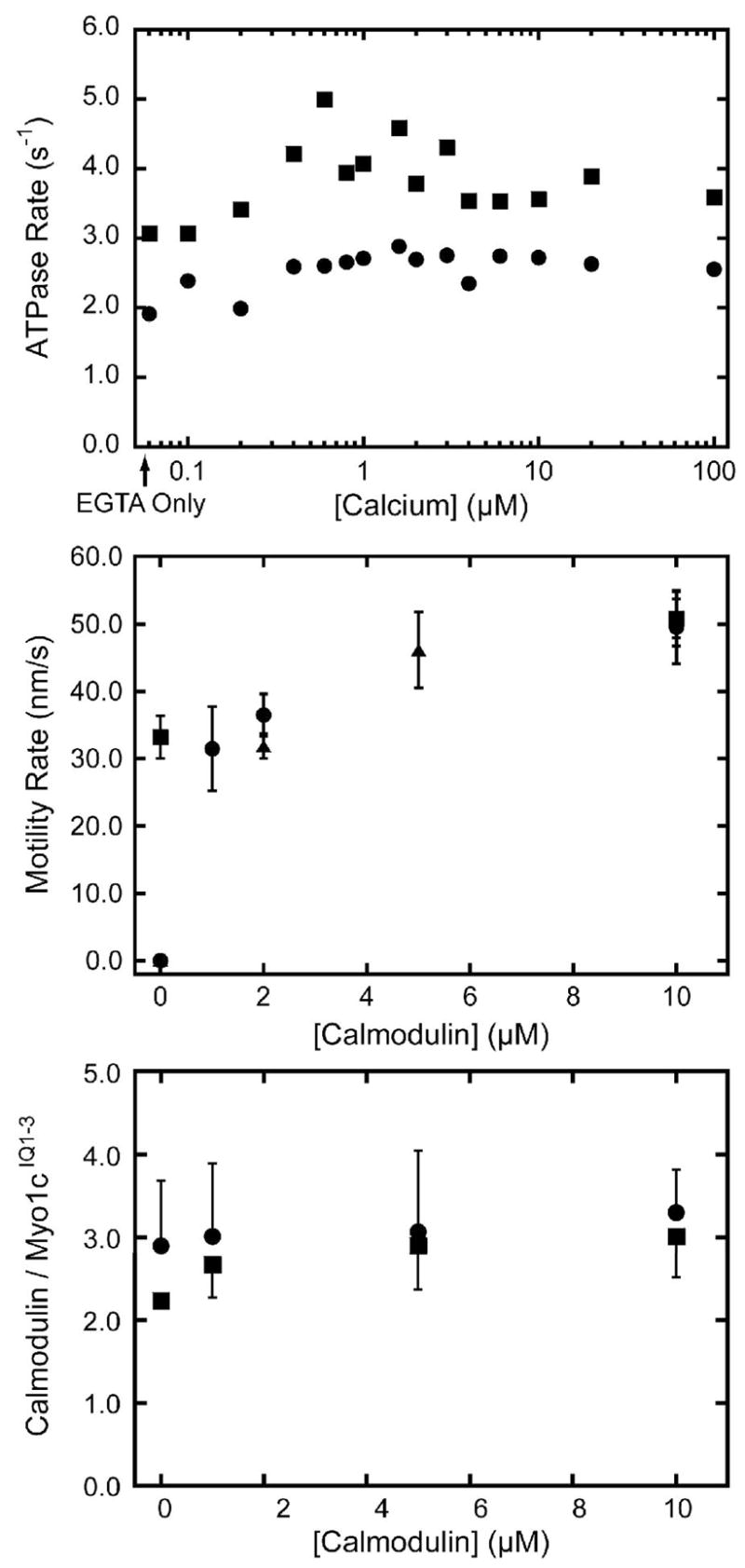
(Top) Actin-activated ATPase activity of 100 nM myo1cIQ1-3 in the presence of 50 μM actin as a function of the concentration of free calcium in the (●) absence and (■) presence of 10 μM calmodulin. The first point represents the ATPase activity in the absence of added calcium. (Center) Velocity of actin filament gliding, measured by the in vitro motility assay, as a function of calmodulin concentration in the (■) absence and presence of (●) 10 μM and (▲) 100 μM free calcium. No motility was detected in the absence of calmodulin and presence of 10 μM or 100 μM calcium. Each point and error bar represents the average and standard deviation of 50 filaments (Bottom) Number of calmodulin molecules bound to myo1cIQ1-3 as a function of calmodulin concentration in the (●) absence and (■) presence of 100 μM free calcium. The calmodulins bound at the zero point co-purifed with the myosin. Error bars represent the range of duplicate experiments.
