Fig. 1.
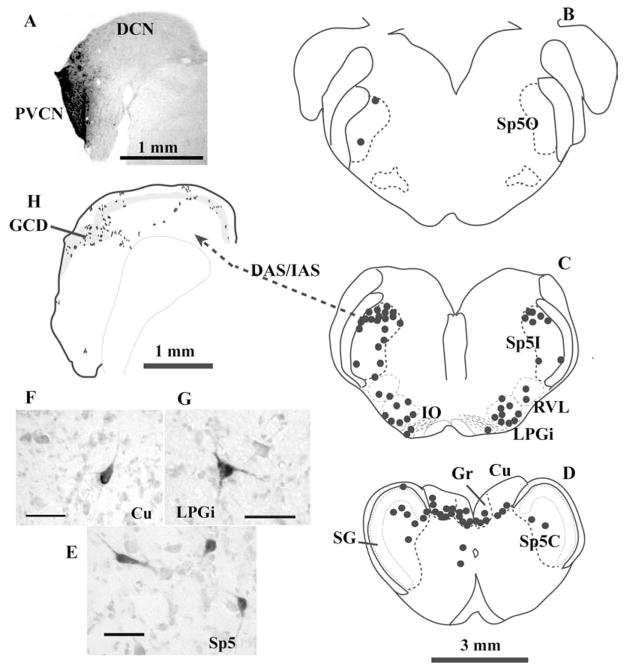
Projections from Sp5 to the CN in the guinea pig. (A–G) Retrograde labeling in the brainstem after an injection of biotinylated dextran amine (BDA) into the CN. (A) Photomicrograph of the injection site. The injection site is virtually restricted to the shell region of the PVCN. (B–D): Drawings of 1 mm transverse sections across the medulla. Each dot represents one labeled cell. The labeled neurons are located primarily on the ipsilateral side of Sp5, in the Sp5I and Sp5C. Very few labeled cells, if any, are located in the SG (D). Labeled neurons can also be found in the medular reticular formation (RVL and LPGi, C), inferior olive (IO, C), and dorsal column nuclei (Gr and Cu, D). Projection neurons in Sp5 have either polygonal or elongated somata (E). Projection neurons in dorsal column nuclei and reticular formation are multipolar (F and G). (H) Terminal labeling in the CN after placement of an anterograde tracer into Sp5I. Most Sp5 fibers enter the CN via DAS/IAS and terminate primarily in the GCD (gray area), but also in deep DCN. Each dot represents one to three labeled terminal endings. Scale bars = 25 μm (E–G). (Abbreviations: CN, cochlear nucleus; Cu, cuneate nucleus; DAS, dorsal acoustic striae; DCN, dorsal cochlear nucleus; GCD, granule cell domain; Gr, gracile nucleus; IAS, intermediate acoustic striae; IO, inferior olive; LPGi, lateral paragigantocellular reticular nucleus; PVCN, posteroventral cochlear nucleus; RVL, rostral ventrolateral reticular formation; SG, subnucleus gelatinosus; Sp5, spinal trigeminal nucleus; Sp5C, pars caudalis of Sp5; Sp5I, pars interpolaris of Sp5; Sp5O, pars oralis of Sp5).