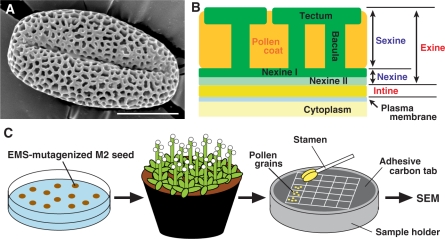
Fig. 1.
Surface structure of mature pollen grains of wild-type Arabidopsis and the strategy used for mutant screening. (A) Wild-type pollen grains observed by SEM. The reticulate sculpture of exine can be observed. Bar = 10 μm. (B) Diagram of the pollen surface structure composed of inner intine, outer exine, and pollen coat filling the cavities of the exine sculpture. Exine is divided into sexine (outermost tectum and column-like baculae) and nexine (nexine I and innermost nexine II). (C) Procedure for mutant screening. M2 seeds were sown on an agar plate and grown for 2 weeks, and then seedlings were transplanted to vermiculite and grown to maturity. When flowers opened, a stamen was detached from a fully opened flower of each plant and pollen grains were put on an SEM sample holder. After coating with Pt and Pd, the surface structure of the pollen grains was observed by SEM.