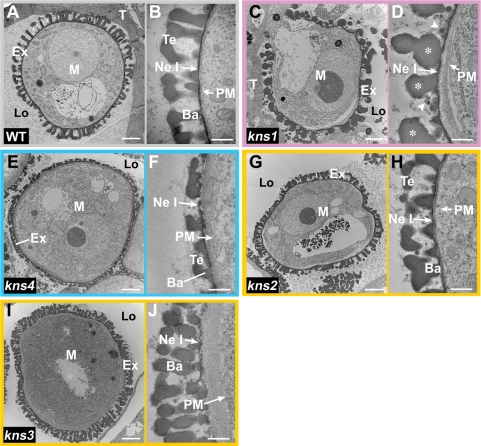
Fig. 4.
Exine structure in kns microspores. Transmission electron micrographs indicating cross-sections of wild-type and kns microspores at the bicellular stage. (A, B) Wild type (Ler). Exine construction has been completed except for nexine II. (C, D) kns1. Deformed baculae (asterisks) can be observed, but tectum is missing. Many globular structures (arrowheads) appear on the surface of nexine I. (E, F) kns4. The exine structure of kns4 is less than half the thickness of wild-type exine. (G, H) kns2. (I, J) kns3. Microspores of these mutants are surrounded by densely distributed baculae. Bars = 2 μm (A, C, E, G, I) and 0.5 μm (B, D, F, H, J). Ba, bacula; Ex, exine; Lo, locule; M, microspore; Ne I, nexine I; PM, plasma membrane; T, tapetal cell; Te, tectum.