Figure 2. Coordination of the DARGG loop carbonyl crown.
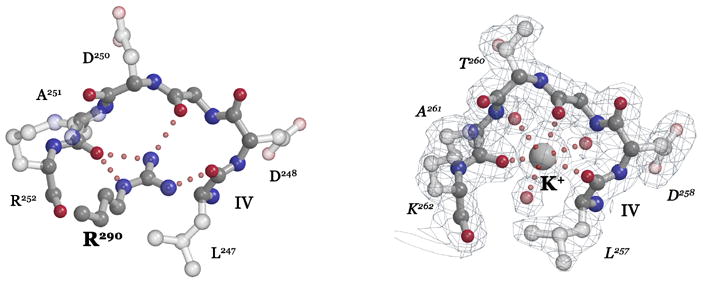
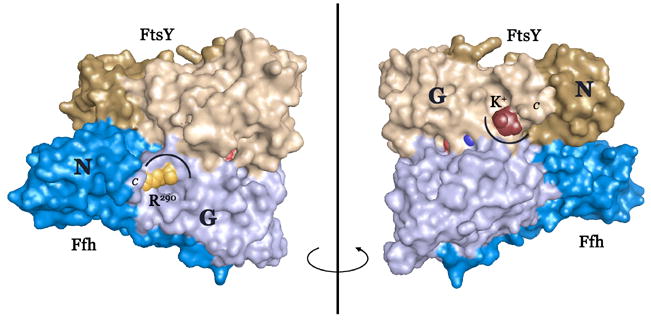
(A) In Ffh (left), Arg290 forms an extensive set of hydrogen bonding interactions with the carbonyl oxygens of the Ffh DARGG loop (which has the sequence Asp250AlaArgGlyGly254 in T. aquaticus Ffh). In FtsY (right), a potassium ion (large ball) is coordinated by the carbonyl crown contributed by motif IV/DARGG residues Leu257, Gly259 and Ala261, and by three water molecules (small red balls). The 2Fo−Fc electron density map is shown with the backbone atoms of residues 257–262 in ball-and-stick. The ‘DARGG’ loop has the sequence Thr260AlaLysGlyGly264 in T. aquaticus FtsY. (B) The context of the DARGG loop interactions in (A) are shown in two orientations of a surface representation of the heterodimer. The interactions are at the junction of the N and G domains of each protein, and in Ffh, couple to the position of the C-terminal helix (which in the intact protein is linked to the signal sequence recognition subunit, the M-domain). The C-terminus is indicated (C), and the DARGG loop indicated in each case by an arc. The figure was made with PYMOL (DeLano, 2002).
