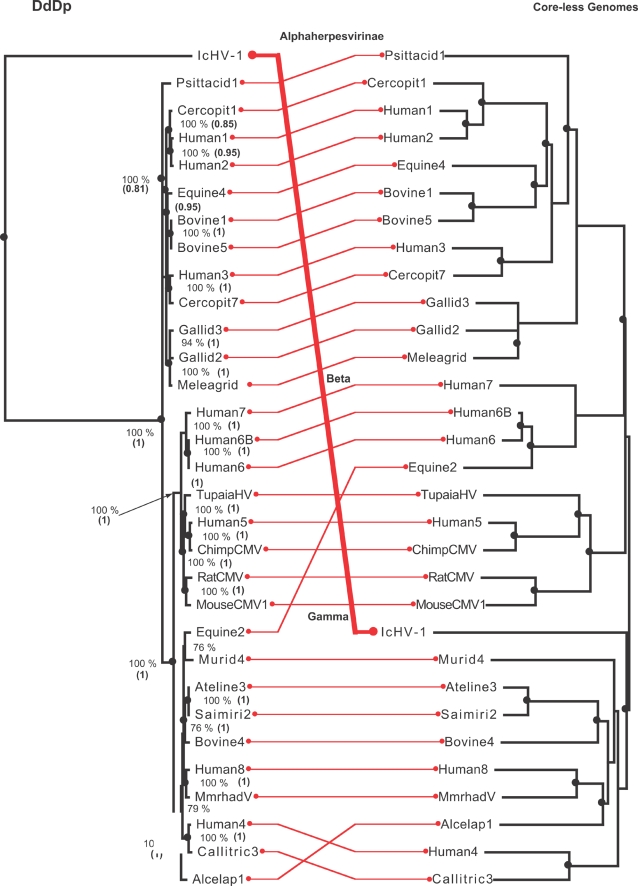
Figure 3. Assemblage of a herpesvirus DNA-dependent-DNA polymerase (DdDp or cores) maximum likelihood tree rooted with the Ictalurid virus (IcHV-1) infecting the Channel catfish (right) and a phenogram clustered with the neighbor-joining method implemented in the Weighbor program for herpesvirus “core-less” genomes, i.e., without the DdDp (including satellite functions) rooted at the Alpha-herpesvirus (Alphaherpesvirinae) that infect birds and mammals (right).
In spite of the IcHV-1 being distantly related to the herpesvirus and of questionable membership in the Herpesviridae family, it shares several satellite functions with the Beta and Gammaherpesvirinae infecting tetrapods. Nodes encircled by black dots indicate co-divergence events. Values near the nodes of the DdDp indicate the number of times that each tree component was observed during 500 non-parametric bootstrap maximum likelihood iterations with phyml, value between parenthesis are the posterior Bayesian probability of the node estimated with MrBayes. Nodes encircled by black dots indicate codivergence events estimated with the TreeMap program.