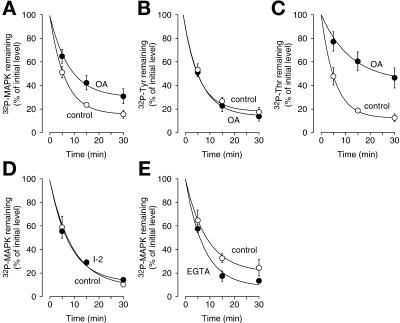
Figure 11.
Effects of various inhibitors on p42 MAPK* dephosphorylation in CaCl2-treated CSF extracts. CSF extracts were preincubated with okadaic acid (1 μM; A–C), I-2 (40 U/μl; D), or EGTA (10 mM; E) for 5–10 min on ice. CaCl2 (0.4 mM) and p42 MAPK* (50 nM) were added simultaneously (CaCl2 was replaced with water for EGTA-treated extracts), and aliquots were taken at various times. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Data are shown as mean values ± SEM for n experiments as indicated below. (A) Okadaic acid–induced inhibition of p42 MAPK* dephosphorylation (n = 4) is shown. (B and C) Okadaic acid inhibits p42 MAPK* threonine dephosphorylation (C) but does not affect tyrosine dephosphorylation (B). Samples were subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis and quantified (n = 4). (D) PP1 activity is not required for p42 MAPK* dephosphorylation (n = 3). I-2 (40 U/μl) was used to inhibit PP1. The same concentration of I-2 inhibited DNA replication (our unpublished results). (E) EGTA does not inhibit p42 MAPK* dephosphorylation (n = 3).