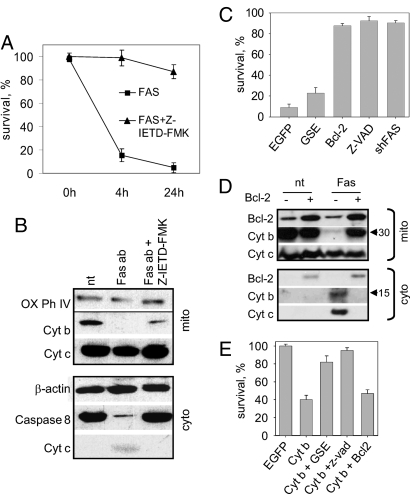
Fig. 3.
Place of Cyt b in the FAS apoptosis pathway. (A) Caspase 8 is required for FAS-induced apoptosis. Cell survival was measured in HeLa cells by methylene-blue staining following treatment (at time 0 h) with FAS agonistic antibody or FAS antibody plus Z-IETD-FMK (specific caspase 8 inhibitor). Three independent experiments were performed; error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) Inhibition of Caspase 8 during FAS-induced apoptosis prevents Cyt b processing. Mitochondrial (Top) and cytoplasmic (Bottom) fractions were prepared from untreated HeLa cells (nt) or 8 h after treatment with FAS antibody plus cycloheximide (CHI) (Fas ab) in the absence or presence of Z-IETD-FMK. Western blotting used the indicated antibodies including β-actin and Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit IV as cytoplasmic and mitochondrial markers, respectively. (C) FAS apoptosis can be blocked by expression of GSE F21 or Bcl-2 and requires caspase and FAS activity. HeLa cells expressing EGFP (control), GSE F21, Bcl-2, or shFAS were treated with FAS antibody. Uninfected HeLa cells were treated with FAS antibody plus Z-VAD. Survival was measured by methylene-blue staining 4 h after treatment and is shown for each cell type relative to the same cells in the absence of FAS antibody. Here and in (E), three independent experiments were performed: error bars indicate standard deviations. (D) Western blot analysis of HeLa mitochondrial (left) and cytoplasmic (right) fractions 12 h after treatment with FAS antibody (nt, untreated). Cells were infected before treatment with control or Bcl-2 lentiviruses. (E) Cyt b-induced cell death can be blocked by GSE F21 or Z-VAD, but not Bcl-2. HeLa cells were infected with EGFP (control), Cyt b, GSE F21, and Bcl-2 lentiviral constructs. Z-VAD was added 24 h after infection and methylene-blue staining was performed 48 h after infection.