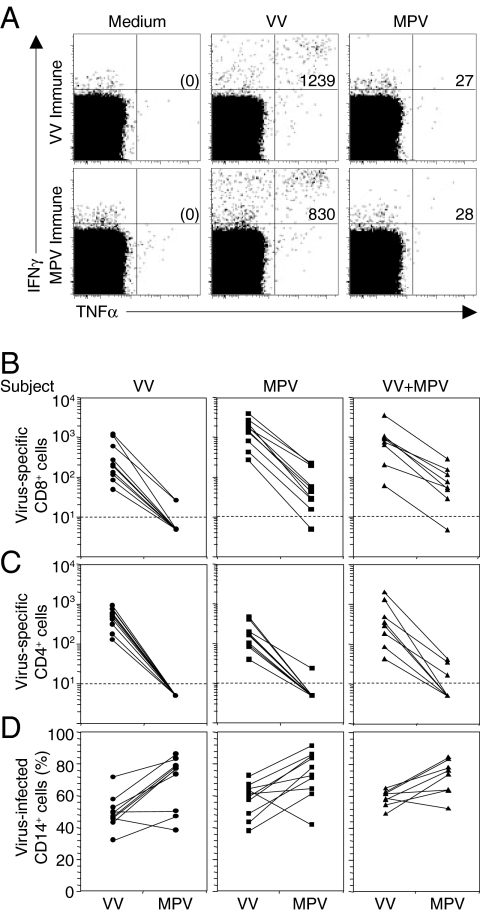
Fig. 1.
MPV immune evasion from orthopoxvirus-specific T cells. (A) Antiviral CD8+ T cell responses from a VV-immune (6 months post-VV infection) or a MPV-immune (4 months post-MPV infection) subject were measured by ICCS after 18 h of stimulation with VV or MPV (MOI of 0.3) with Brefeldin A added for the last 6 h of stimulation. PBMCs were gated on CD8β+CD4− T cells. The numbers in the upper right quadrants depict the frequency of virus-specific IFNγ+TNFα+ T cells per million CD8+ T cells identified after background subtraction from control wells containing Medium alone (shown in parenthesis). (B) Virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses against VV or MPV were determined as in A, using PBMCs from VV-immune subjects (VV; 4–6 months postinfection, n = 10), MPV-immune subjects (MPV; 3–31 months post-MPV infection, n = 10) or VV-immune subjects who contracted MPV infection (VV+MPV; 3–13 months post-MPV infection, n = 8). (C) Virus-specific CD4+CD8β− T cell responses against VV or MPV were determined as in A. (D) Monocytes were identified based on forward and side scatter characteristics and CD14 surface expression. The percentage of CD14+ monocytes infected with VV or MPV was determined after 18 h of infection, using a polyclonal anti-orthopoxvirus antibody (40).