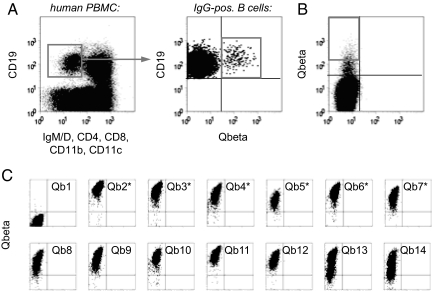
Fig. 2.
Screening for Qβ-specific antibodies. (A) Isolation of Qβ-specific B cells by FACS. Human PBMC were stained for the presence or absence of the indicated surface markers and analyzed for expression of Qβ-specific antibodies. IgM-IgD-negative, isotype switched B cells (as gated in Left) specifically binding to Qβ (as gated in Right) were sorted for library construction. (B) Sorting of BHK cells displaying Qβ-specific antibodies. BHK cells were infected at a low MOI with a Sindbis virus library encoding scFv antibodies constructed from Qβ-specific B cells. After staining with Alexa 647 nm-labeled Qβ, cells displaying specific antibodies were sorted onto semiconfluent BHK feeder cells (1 cell per well). (C) Rescreening for Qβ-specific antibodies. Two to three days after sorting, BHK cells showing signs of viral infection were analyzed for binding to Qβ. The first 14 of the 276 wells analyzed are shown. Antibodies expressed by those clones indicated with an asterisk were selected for gene rescue and sequencing.