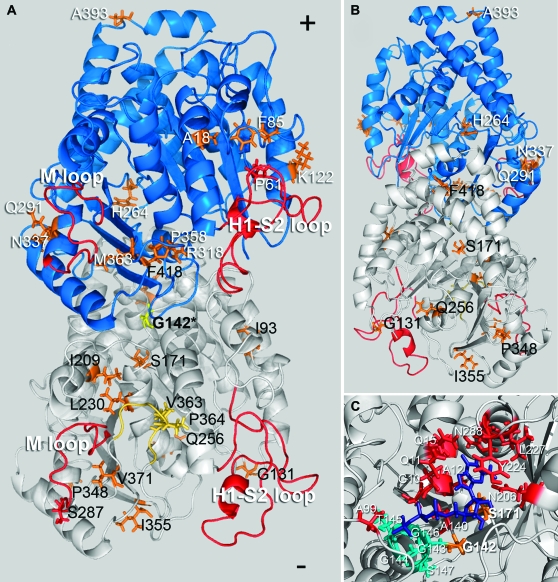
Figure 3.—
Location of compensatory mutations obtained from the G142S line mapped on a model of the Toxoplasma tubulin dimer (the α1-subunit is white and the β1-subunit is blue). The G142S mutation (yellow) is located in the GTP-binding domain of α-tubulin. (A) Most mutations (orange/yellow) are on the surface of the dimer that faces the inner lumen of the microtubule. Secondary mutations in α1-tubulin (black text) occur at I93V, G131R, S171A, I209V, L230V, Q256H, S287P, P348L, I355E, V363A, P364R, V371G, and F418I. Suppressors in the β1-tubulin subunit (white text) occur at residues A18P, P61A, F85L, K122E, H264Q, Q291E, R318C, N337T, P358R, M363V, and A393V. G142S α1-tubulin mutations at V363A and P364R occur in the α-tubulin-specific insert (yellow). (B) The α1-tubulin mutation at Q256 and the β1-tubulin mutation at H264 are the only mutations that face the outer surface of the dimer within the microtubule lattice. The β-subunit mutation A393V is located at the dimer–dimer interface within the protofilament. (C) The primary resistance mutation at G142 is located within the tubulin motif (teal) of the α-tubulin GTP-binding site. The GTP moiety is purple and residues contributing to GTP binding outside of the GGGTGS tubulin motif are red. The primary mutation G142S is located in the binding site and interacts with the α-phosphate. The S171A mutation also locates to the binding site; S171 interacts with the ribose portion of GTP (Gigant et al. 2000; Lowe et al. 2001).