Figure 1.
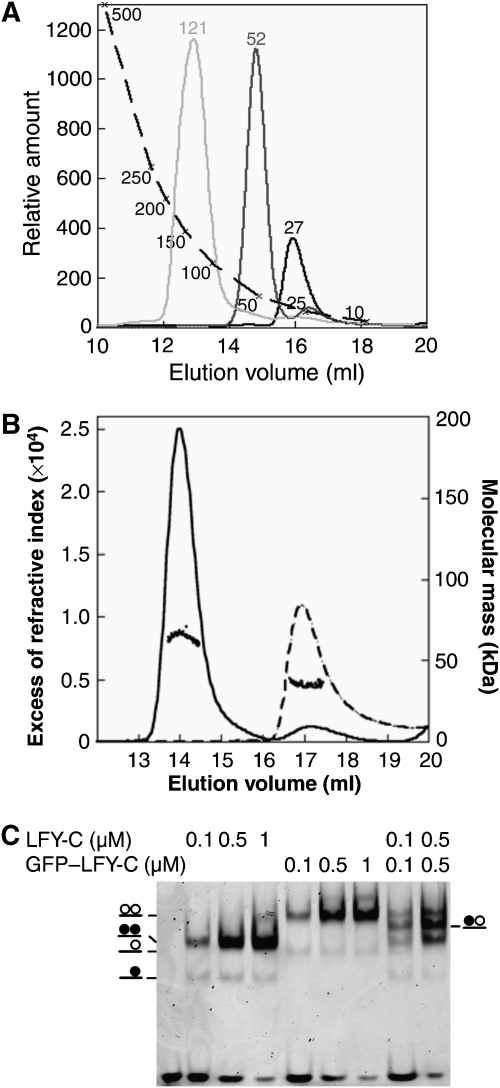
DNA-dependent dimerization of LFY-C. (A) Size-exclusion chromatography. LFY-C (40 μM, black curve), AP1 DNA (10 μM, dark grey curve), LFY-C (40 μM)+AP1 DNA (10 μM, light grey curve) were analysed. LFY-C elution at a volume corresponding to 28 kDa is consistent with the monomer size (25.7 kDa), the DNA duplex elutes earlier than expected at a volume corresponding to 52 kDa because of its elongated shape. The LFY/DNA complex elutes at a volume corresponding to 121 kDa. Molecular weights estimated from the calibration curve (dashed line) are indicated. (B) Molecular mass of LFY-C alone (dashed line) or in combination with AP1 DNA (solid line) determined by multi-angle laser light scattering and refractometry combined with size-exclusion chromatography. Elution profiles were monitored by excess refractive index (left ordinate axis). Dots show the molecular mass distribution (right ordinate axis). Average molecular mass is 64±2 kDa for the LFY-C/DNA complex (65 kDa theoretical size for a dimeric complex) and 35±1 kDa for LFY-C alone (26 kDa theoretical size for LFY-C monomer). (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) with 10 nM AP1 DNA and various LFY-C or GFP–LFY-C concentrations. Schematic complexes with LFY-C (filled circle) and GFP–LFY-C (open circle) are depicted.