Fig. 2.
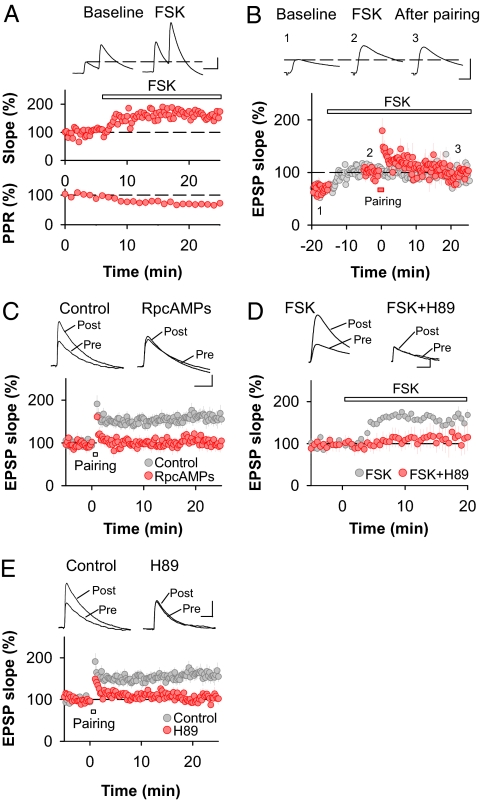
Activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway is necessary and sufficient for presynaptic LTP. (A) Forskolin (50 μM) enhances synaptic transmission (n = 5) and decreases PPR (n = 5) at cortico-amygdala synapses. (Scale bars: 5 mV and 50 ms.) (B) LTPFSK of synaptic transmission occludes the induction of LTPHA (n = 5). Gray symbols represent LTPFSK in the absence of LTPHA induction (same data as in A). Averaged sample traces were taken at the time points indicated by the numbers. (Scale bars: 5 mV and 10 ms.) (C) Induction of LTPHA is blocked by the nonhydrolyzable cAMP analog Rp-cAMPS (100 μM) (control, n = 18; Rp-cAMPS, n = 6). (Scale bars: 2 mV and 50 ms.) (D) LTPFSK requires activation of PKA. Bath application of the PKA antagonist H-89 (20 μM) completely abolishes the effect of FSK on synaptic transmission (control, n = 5; H-89, n = 5). (Scale bars: 2 mV and 50 ms.) (E) Induction of LTPHA at cortico–LA synapses is blocked by the PKA antagonist H-89 (20 μM) (control, n = 18; H-89, n = 8). (Scale bars: 2 mV and 50 ms.) Error bars, ±SEM.