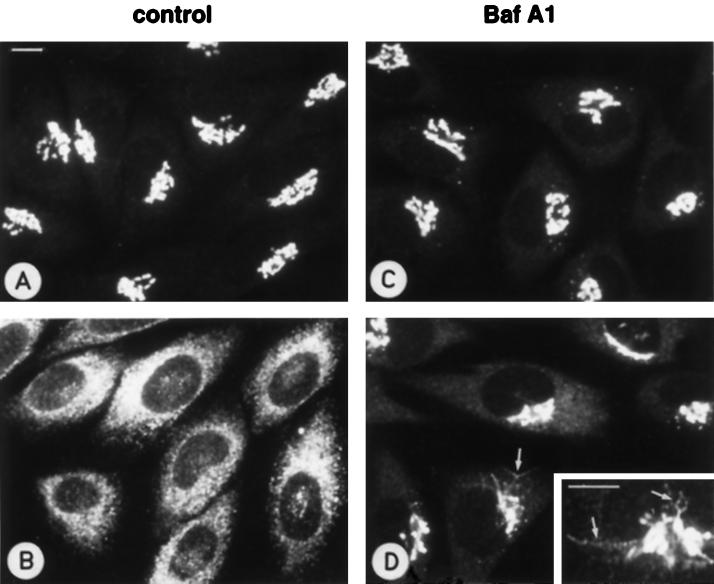
Figure 1.
Baf A1 inhibits the BFA-induced redistribution of Golgi mannosidase II to the ER. Control NRK cells (A and B) and cells pretreated for 3 h in medium containing 10−6 M Baf A1 (C and D) were either fixed directly (A and C) or after a further 10 min incubation in the presence of BFA (1 μg/ml) (B and D), followed by staining with antibodies against mannosidase II. In control cells, BFA causes an efficient relocation of mannosidase II to the ER (B), whereas in Baf A1-treated cells the redistribution of the protein is considerably slowed down (D). Accordingly, tubular intermediates of the transfer process can be observed (D and inset; arrows). The cells in D also display weak ER-like staining, indicating that the retrograde transport of mannosidase II is not completely blocked by Baf A1. Bars, 10 μm.