Figure 10.
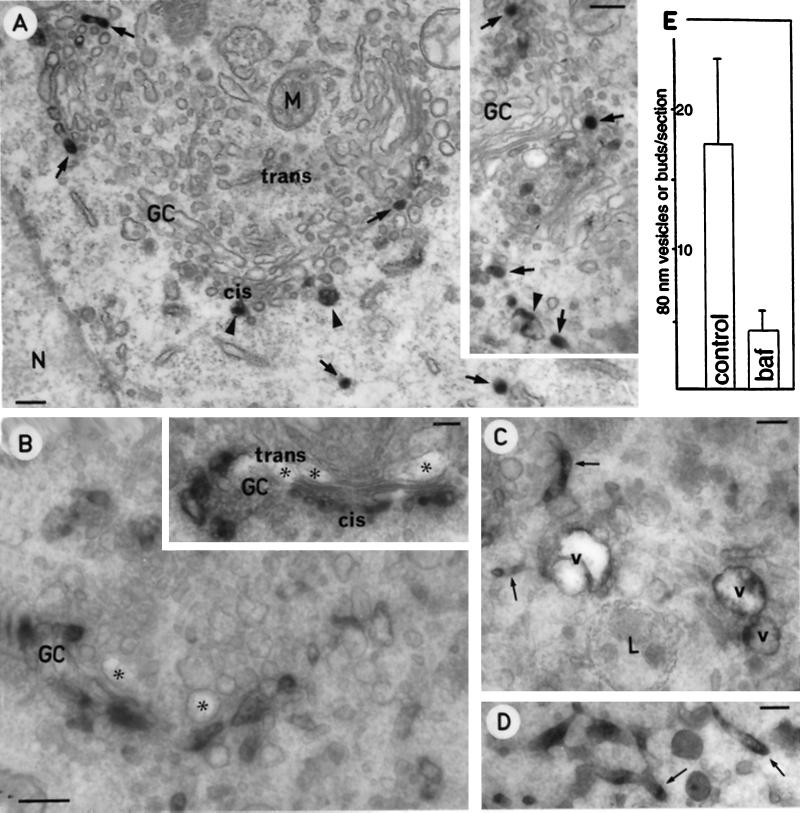
Baf A1 inhibits the formation of p58-containing 80 nm (COPI) vesicles. Control and Baf A1-treated PC12 cells were stained with antibodies against p58 and processed for immunoperoxidase electron microscopy. (A and inset) Control cells showing the presence of p58 in both cisternal and pleiomorphic elements (arrowheads) and a number of ∼80 nm vesicles or buds (arrows) at the cis face of the Golgi complex (GC). (B–D) In Baf A1-treated cells the cisternal organization and polarity of the Golgi are maintained, but both trans-elements (asterisks) and p58-positive cis-elements appear dilated. In spite of the more intensive staining of the cis-Golgi cisternae (B and inset), the p58-positive 80 nm vesicles are largely absent. C and D show p58-positive vacuoles (v) and tubules (arrows) observed in the drug-treated cells. (E) Quantitation showing that Baf A1 considerably reduces the number of p58-positive 80 nm vesicles and buds. A (inset) and B (inset)–D correspond to ∼50 nm and ∼200 nm sections, respectively. N, Nucleus; M, mitochondria. Bars, 0.2 μm.