Figure 7.
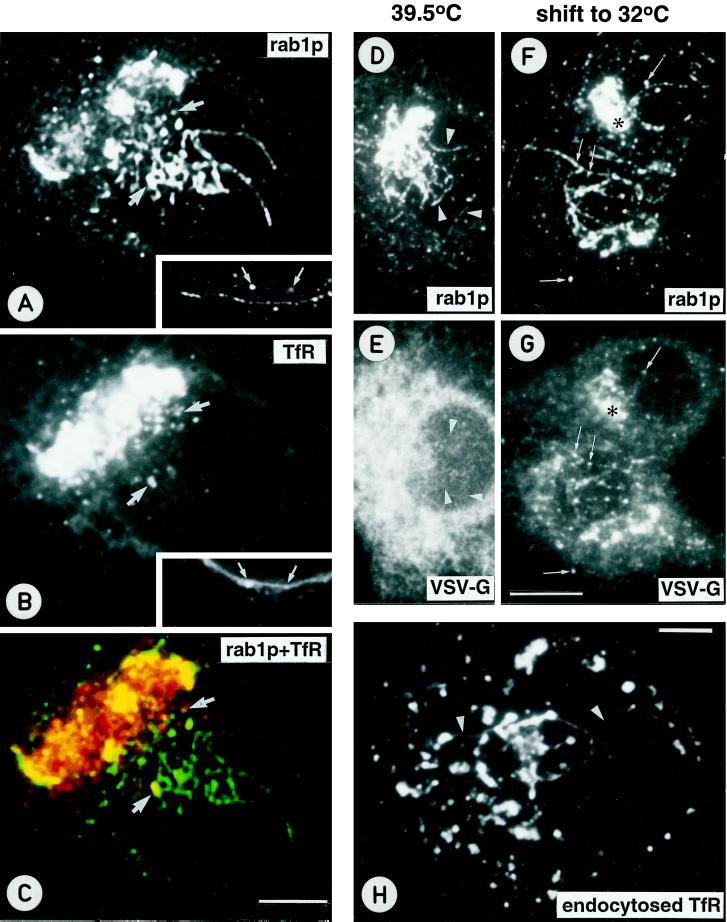
Newly synthesized, anterogradely transported proteins are not concentrated in the pre-Golgi tubules accumulating in Baf A1-treated cells. (A–C) BHK-21 cells were infected with an SFV vector encoding the human TfR, treated with Baf-A1, and double-stained for rab1p (A) and TfR (B). C shows the merged confocal image. Partial colocalization of rab1p and TfR is observed in the punctate pre-Golgi structures (arrows), whereas both central and peripheral (see insets in A and B) rab1p-positive tubules do not contain detectable amounts of TfR. (D–G) Double-localization of rab1p (D and F) and the VSV-G protein (E and G) in tsO45 mutant-infected, Baf A1-treated cells incubated for 3 h at 39.5°C (D and E) or shifted for an additional 5 min to 32°C in the continuous presence of the drug (F and G), to synchronize the export of the G protein from the ER. At 39.5°C, the bulk of the G protein remains arrested in the ER and is not detected in the rab1p-positive tubules (arrowheads in D and E). In cells shifted to 32°C, the G protein and rab1p partially colocalize in the Golgi region (asterisk) and many of the punctate pre-Golgi structures (arrows), whereas the rab1p-positive tubules remain mostly devoid of the G protein. (H) To study the effect of Baf A1 on endocytic compartments, BHK-21 cells expressing human TfR were incubated in medium containing mouse anti-TfR antibodies. After Baf A1-treatment the cells were fixed, and the internalized TfR-antibody complexes were visualized using fluorochrome-coupled secondary antibodies. Note the tubular connections between peripheral and central endocytic structures (arrowheads). Bars, 5 μm (A–C, H) and 10 μm (D–G).