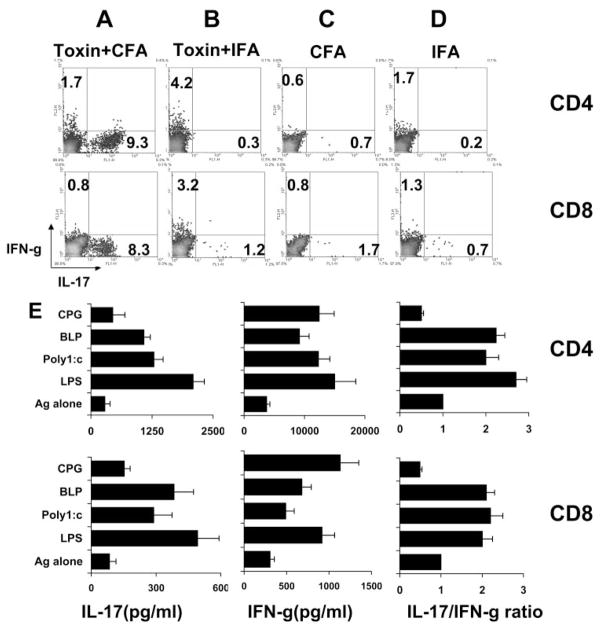
Figure 5.
The role of CFA, pertussis toxin, and TLR ligands in the induction of IL-17+ IRBP-specific T cells. Synergistic effect of CFA and PTX on the induction of IL-17+ IRBP-specific T cells in vivo. B6 mice were immunized with IRBP1–20 emulsified in CFA (A, C) with (A) or without (C) PTX pretreatment or in IFA (B, D). CD4 and CD8 T cells were prepared at p.i. day 13 and were stimulated with immunizing peptide for 4 days. Activated T cells were separated by Ficoll, intracellularly stained with the indicated antibodies, and analyzed by FACS analysis. (E) In vitro effect of TLR ligation of BMDCs on IL-17 and IFN-γ production. In vivo-primed unfractionated IRBP-specific T cells were incubated for 3 days with immunizing peptide and APCs (BMDCs), which had been left untreated or were treated for 18 hours with the TLR ligands, BLP (TLR2, 5 μg/mL), LPS (TLR4, 1 μg/ mL), poly(I:C) (TLR3, 50 μg/mL), or CpG1826 (TLR9, 10 μg/mL). IL-17 and IFN-γ production was measured by ELISA (left and center) and the IL-17/IFN-γ ratio was calculated.