Figure 3. Catalytically-active and -inactive cath-D are released early in etoposide-induced apoptosis.
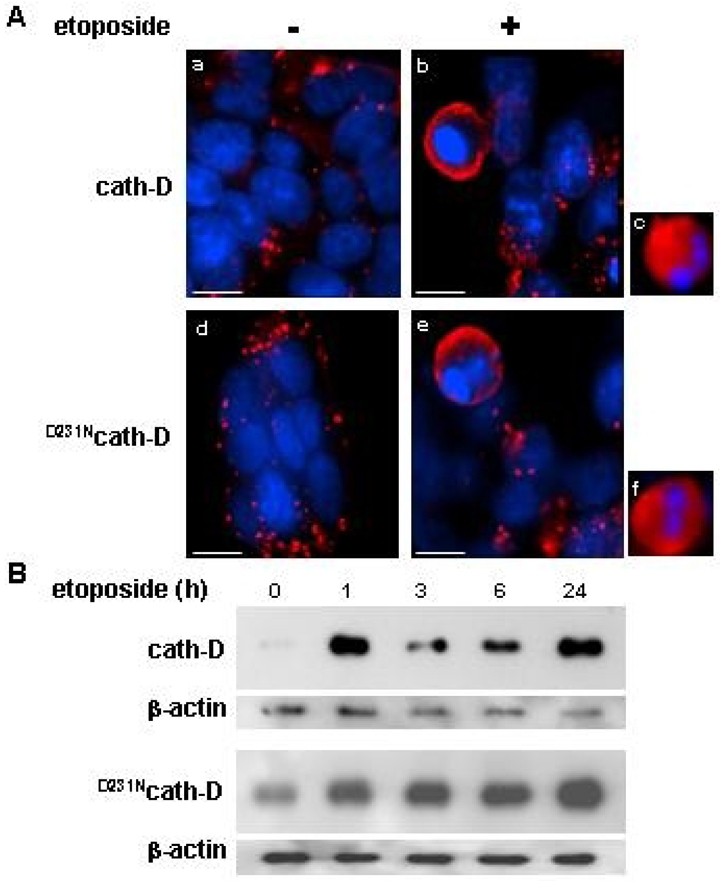
(A) Immunofluorescence of cath-D. Cells were either exposed to 10 μM etoposide for 24 h (b, c, e, f) or left untreated (a, d). Cells were incubated first with anti-human cath-D M1G8 mouse monoclonal antibody followed by a RITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody. Bars, 7.4 μM. (B) Release of cytosolic cath-D. Western blotting of wild-type cath-D (top panel) and D231Ncath-D (bottom panel) in cytosols extracted from cells either exposed to 10 μM etoposide. Cytosol was extracted using 20 μg/ml and 45 μg/ml digitonin for cath-D and D231Ncath-D cells, respectively, for 10 min as previously described (11). Cath-D immunoblotting was performed using an anti-human cath-D monoclonal mouse antibody followed by an anti-mouse peroxidase-conjugated antibody.
