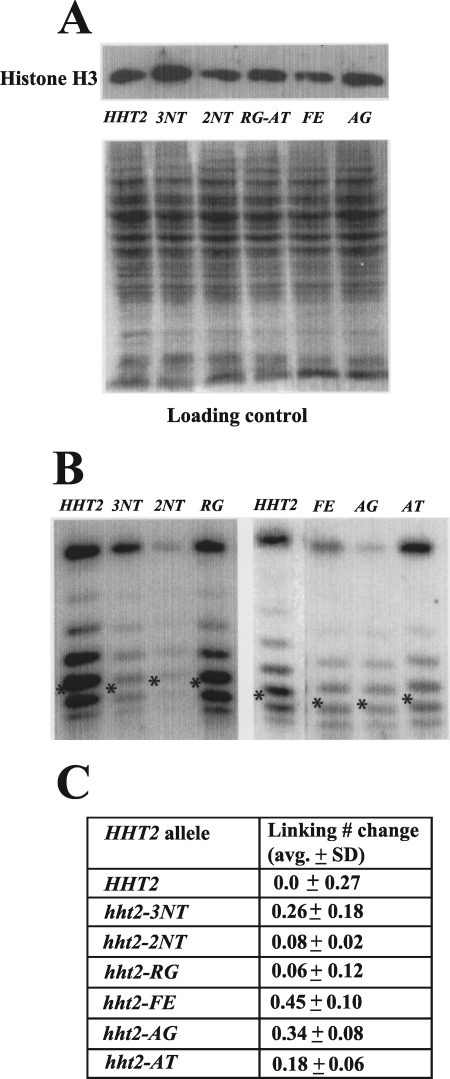
FIG. 5.
Histone H3 mutations do not grossly affect protein level or nucleosome structure. (A) Histone mutants are expressed at levels similar to that of wild-type histone H3. Cell lysates from yeast strains harboring wild-type histone H3 (RMY331) or the indicated mutants (RMY332, RMY333, RMY335, RMY336, and RMY338) were electrophoresed in a 10% polyacrylamide gel, subjected to Western blotting, and visualized using an antibody against the C terminus of histone H3. The loading control was done by staining the SDS-PAGE gel after protein transfer. (B) Histone mutations cause little change in minichromosome topology. Genomic DNAs from strains harboring URA3-ARS1 and expressing wild-type histone H3 (RMY341) or the indicated H3 mutants (RMY342 to -347) were extracted using glass beads. DNA samples were run in a 1.5% agarose gel containing 40 μg/ml chloroquine; following Southern blotting, the minichromosomes were visualized using a probe corresponding to the URA3 coding sequence. Asterisks indicate the center of the Gaussian distribution of topoisomers. The band at the top of each lane is nicked circular URA3-ARS1 plasmid, and faster-migrating topoisomers represent more positively supercoiled species. (C) Linking number change (toward more positively supercoiled values) of the URA3-ARS1 minichromosome in yeast harboring the indicated histone H3 mutants relative to that in the wild type. Averages and SD were determined using at least three independent clones.