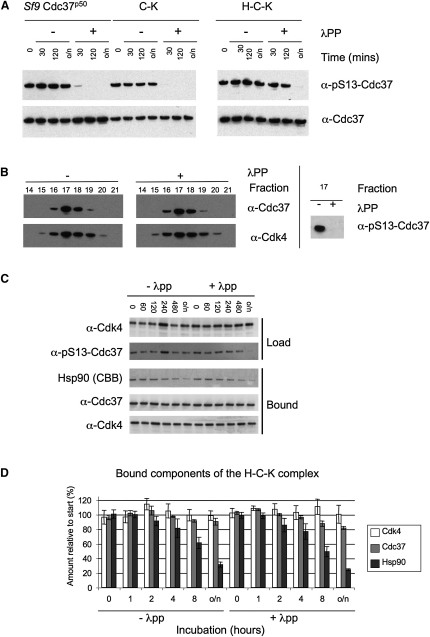
Figure 2.
Dephosphorylation of Free Cdc37 or Cdc37 within the C-K and H-C-K Complexes by λPP
(A) The rate of dephosphorylation of free Cdc37, the C-K complex, and the H-C-K complex were compared. Samples with approximately equivalent amounts of Cdc37 were incubated in the absence (−) and presence (+) of λPP at room temperature for the specified times. Western blots were probed with α-pSer13-Cdc37. The blots were stripped and reprobed with α-Cdc37 as a loading control.
(B) The C-K complex was incubated in the absence (−) and presence (+) of λPP and the effect of dephosphorylation on composition examined by analytical gel filtration with a Superose 6 10/300 GL column; 1 ml fractions were probed for each component of the complex by Western blot. Dephosphorylation was confirmed by probing with α-pSer13-Cdc37. Cdk4 alone elutes in fraction 19 (data not shown).
(C) The H-C-K complex was incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of λPP. At specified time points, samples were withdrawn and the effect of dephosphorylation on complex stability assessed by pulldown of the complex via the His6-tagged Cdk4 on Talon resin. Samples were probed by Western blot for Cdc37 and Cdk4 and Coomassie stain for Hsp90. Dephosphorylation of the coprecipitated samples was confirmed by probing with α-pSer13-Cdc37.
(D) The experiment was repeated in triplicate, and the amount of the components precipitated by the Talon resin (Bound) relative to the start of the incubation, was determined by densitometry of the Western blots for Cdk4 and Cdc37, or the Coomassie-stained PAGE gel for Hsp90. Error bars indicate SD of the measurements.