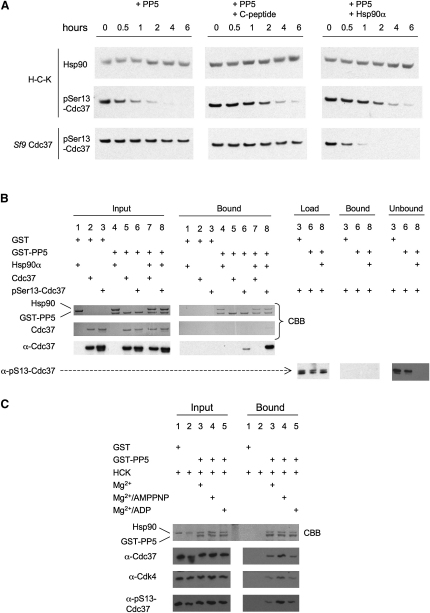
Figure 3.
Dephosphorylation of Cdc37 by PP5 In Vitro
(A) H-C-K complex or Sf9-expressed Cdc37 was incubated with PP5 at room temperature and the extent of dephosphorylation at specified times assessed by probing Western blots with α-pSer13-Cdc37. This experiment was repeated in the presence of a 10-fold molar excess of PP5 activator—either a seven residue peptide (SRMEEVD) corresponding to the TPR binding motif of Hsp90 or full-length human Hsp90α.
(B) The interaction of PP5 with Cdc37 is mediated by Hsp90. GST-tagged PP5 was incubated with Cdc37 or phosphorylated Cdc37 in the presence and absence of Hsp90 at 4°C. A small fraction of pSer13-Cdc37 is found in complex with GST-PP5, but the majority of Cdc37 remains phosphorylated; this interaction is significantly increased in the presence of Hsp90, and coincides with an increase in PP5 activity toward Cdc37 (Unbound, lanes 6 and 8). The affinity of GST-tagged PP5 for Hsp90-bound Cdc37 is low compared with that for Hsp90-bound pSer13-Cdc37 (10% Bound, lanes 7 & 8). CBB = Coomassie Brilliant Blue.
(C) The interaction of PP5 with the H-C-K complex. GST-tagged PP5 was incubated with the H-C-K complex at 4°C, and could coprecipitate all components of the complex. The interaction was stabilized, and the activity of PP5 reduced, by inclusion of AMPPNP, but not ADP.