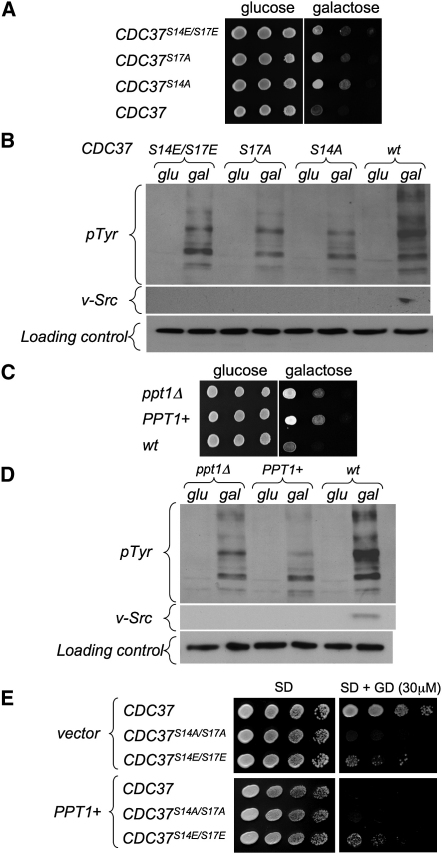
Figure 5.
Effects of Cdc37 Mutation and Overexpression/Deletion of Ppt1 on v-Src Expression in Yeast
(A) Growth of wild-type (CDC37) cells and strains with S14A, S17A, or the doubly mutated S14E/S17E Cdc37 containing the toxic vSrc gene controlled by the GAL promoter, on glucose (glu)- or galactose (gal)-containing medium. Both nonphosphorylatable and phosphomimetic mutants of Cdc37 compromise vSrc activation.
(B) The same strains analyzed for total pY and v-Src levels. Appreciable levels of v-Src were only detectable in wild-type cells.
(C) Both the loss (ppt1Δ) and overexpression (PPT1+) of Ppt1p compromise v-Src expression in cells containing the toxic v-Src gene controlled by a GAL promoter.
(D) The same strains analyzed for total pY and v-Src levels. As for Cdc37 phosphorylation mutants, appreciable levels of v-Src were only detectable in wild-type cells.
(E) Overexpression of Ppt1p causes GA sensitivity in yeast. Cells expressing the wild-type (CDC37), nonphosphorylatable (S14A/S17A), or phosphomimic (S14E/S17E) Cdc37p were transformed with either empty vector or the PPT1 overexpression plasmid (MET25-PPT1). A 1:10 dilution series was grown (4 days, 30°C) on SD agar lacking methionine, without or with 30 μM GA. Overexpression of Ppt1 renders cells as sensitive as the nonphosphorylatable S14A, S17A mutant, of Cdc37.