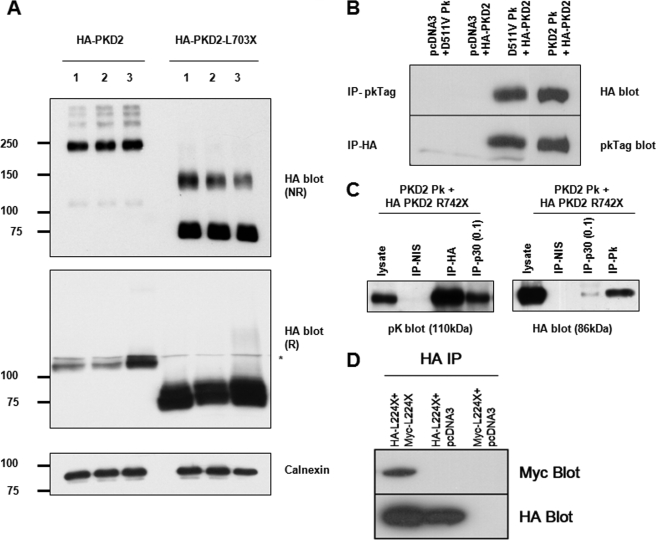
FIGURE 2.
Biochemical evidence for a proximal dimerization sequence in the N terminus of PC2. A, detection of epitope-tagged wild-type and mutant PC2 expressed in HEK293 cells by immunoblotting under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions in three individual samples. Note that both forms of PC2 are detected predominantly as monomers under reducing SDS-PAGE but that there are prominent slower migrating species visible under non-reducing states. For full-length PC2, apart from prominent dimeric species (∼220 kDa), there are also higher bands suggestive of more complex oligomeric structures (e.g. tetramers). For L703X, the monomeric species are more notable than for wild-type PC2 under NR conditions but there is also detectable dimer formation (∼150kDa). Calnexin was used as an endogenous control for loading. * indicates a minor nonspecific band detected by the HA antibody. B, coimmunoprecipitation of epitope-tagged PC2-D511V (D511VPk) and wild-type PC2 (HA-PKD2). PC2-D511V is predicted to retain both hetero- and homodimerization C-terminal domains. C, PC2 mutant lacking both C-terminal dimerization domains (HA PKD2 R742X) associates with wild-type PC2 (PKD2Pk). The p30 and pK antibodies only recognize C-terminal epitope in full-length PC2. However, the HA antibody, which only recognizes the mutant R742X was able to co-IP wild-type PC2 (PKD2Pk) suggesting an interacting sequence proximal to the truncation. 1 mg of total cell lysate was used for IP with HA or NIS (non-immune serum) and 0.1 mg (1/10) for IP with p30 as indicated. 30 μg of lysate were loaded as a positive control. The converse experiment showed that p30 or pK antibodies could pull-down R742X. D, co-immunoprecipitation of HA-tagged N-terminal PC2 protein (NT2) containing the first 223 amino acids (L224X) with co-expressed Myc-tagged L224X. These results implied the existence of an N-terminal dimerization domain.