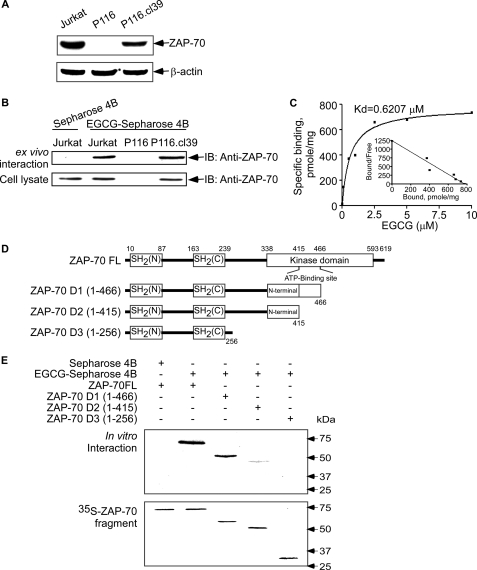
FIGURE 1.
Detection of ZAP-70 protein expression and EGCG binding with ZAP-70 and ZAP-70 deletion mutants. A, expression of ZAP-70 in Jurkat, P116 (ZAP-70-deficient), and P116.cl39 (ZAP-70-restored) cells. ZAP-70 was detected using specific antibodies as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Equal protein loading and protein transfer were confirmed with anti-β-actin. B, ZAP-70-EGCG binding ex vivo. EGCG-Sepharose 4B affinity chromatography was used to pull down ZAP-70 in lysates prepared from Jurkat, P116, or P116.cl39 cells. IB, immunoblot. C, specific binding assay for ZAP-70 and EGCG. The Kd (dissociation kinetic) value of the EGCG-ZAP-70 interaction (Kd = 0.6207 μm) was obtained by using a GST-ZAP-70 affinity-binding assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” D, schematics of ZAP-70 full-length (ZAP-70 FL) and three deletion mutants (ZAP-70 D1, D2, and D3). A series of full-length and deletion mutants of ZAP-70 nucleotide constructs was created as indicated. E, in vitro identification of the EGCG-binding site of ZAP-70. The full-length and deletion mutants of ZAP-70 were translated in vivo with l-[35S]methionine using TnT and subjected to the EGCG-Sepharose 4B pulldown assay.