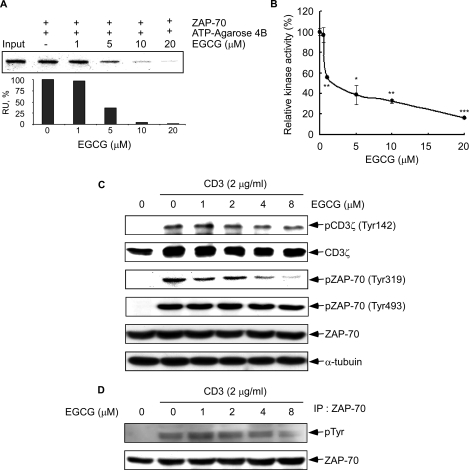
FIGURE 3.
Effect of EGCG on ZAP-70 kinase activity and CD3-induced phosphorylation of ZAP-70. A, EGCG binds to the ATPase catalytic domain of ZAP-70. Active ZAP-70 was incubated with various concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, or 20 μm) of EGCG and ATP-agarose 4B beads in reaction buffer overnight at 4 °C. After washing, the proteins bound with ATP-agarose 4B beads were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot using a ZAP-70 antibody (top) and quantified (bottom) using the ImageJ software program (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda). B, EGCG inhibits ZAP-70 kinase activity in vitro. Kinase activity of ZAP-70 was assayed under the conditions described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are represented as means ± S.D. of triplicate samples from three independent experiments. The asterisk (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.001) indicates a significant decrease in kinase activity compared with untreated control cells. C, phosphorylation of CD3ζ, pZAP-70 (Tyr319), and pZAP-70 (Tyr493) was detected by Western blot as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Equal protein loading and protein transfer were confirmed by stripping and incubating the same membrane with antibodies against α-tubulin, total CD3ζ, or ZAP-70. D, effect of EGCG on CD3-induced ZAP-70 total tyrosine phosphorylation. P116.cl39 cells were starved for 14 h followed by incubation for 1 h with EGCG at different concentrations (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 μm). Cells were washed and then stimulated with 2 μg/ml CD3 for 30 min. Immunoprecipitation with anti-ZAP-70 was followed by anti-phosphotyrosine immunoblot analysis. Membranes were stripped and blotted with anti-ZAP-70.