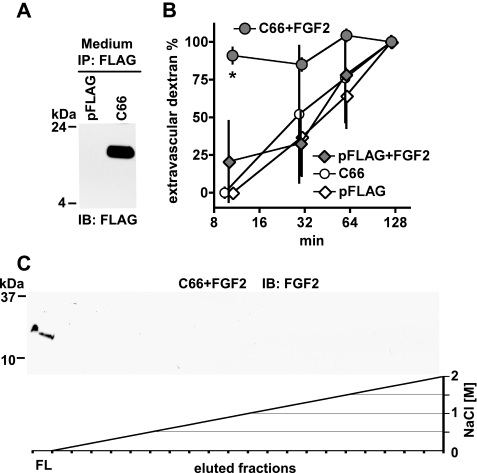
FIGURE 6.
In vitro and in vivo function of the hBP3 FGF binding domain. A, expression of the C-terminal hBP3 fragment that contains the predicted FGF binding domain (C66; see Fig. 1A) in HEK293T cells. Cells were transfected with pFLAG-CMV or C66-FLAG for 48 h and C66 detected by anti-FLAG immunoblot of cell supernatants after anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation. B, heparin affinity chromatography of FGF2 mixed with C66. FGF2 (1 μg) was mixed with C66-FLAG-conditioned medium, and the mixture loaded onto a HiTrap heparin affinity column (see also Figs. 1B and 2B). Bound proteins were eluted by an NaCl gradient. In the presence of C66, FGF2 was not retained by the column and only detected in the flow (FL). C, effect of C66 on vascular permeability in the absence and presence of exogenous FGF2 protein. Chicken embryos were microperfused with a C66-FLAG or a control expression vector (pFLAG). Eight hours after transfection, vascular leakiness was assessed by injection of 40-kDa dextran-FITC without and with a 1-h pretreatment with FGF2 (0.1 μg of perfusion). Extravascular dextran at different time points after dye injection is shown. *, p < 0.05 C66+FGF2 versus pFLAG or C66 or pFLAG+FGF2 (n = 3 per group; analysis of variance).