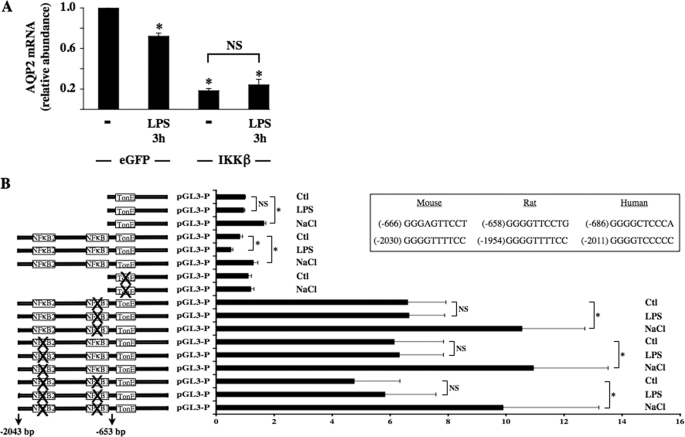
FIGURE 4.
Two κB binding elements located in the AQP2 promoter mediate the decrease of AQP2 transcriptional activity in response to NF-κB activation. A, cells transfected with an expression plasmid that contained either eGFP or constitutively active IKKβ and were stimulated or not for 3 h with 100 ng/ml LPS before RNA extraction. Real-time PCR was performed using primers specific for AQP2. Results are expressed relative to control values determined in cells transfected with eGFP-containing plasmid in the absence of LPS. Bars are the mean ± S.E. from four independent experiments. *, p < 0.05. NS, no significant difference. B, cells were transfected with a luciferase reporter gene 5′-flanked by either the first 517 or 2043 bp of mouse AQP2 promoter, the first 517 bp of mouse AQP2 promoter of which the TonE sequence was mutated, or the first 2043 bp of mouse AQP2 promoter of which either or both putative κB binding sites were mutated. Transfected cells were challenged with either hypertonic (NaCl, 500 mosmol/kg) medium or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h before measurement of luciferase activity. Results are expressed relative to control values determined in cells transfected with luciferase reporter gene 5′-flanked by the first 517 bp of mouse AQP2 promoter and incubated for 24 h in isotonic medium. Bars are the mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; NS, no significant difference. The positions, relative to the start codon, and sequences of putative κB binding sites between different species are shown in the inset. Ctl, control.