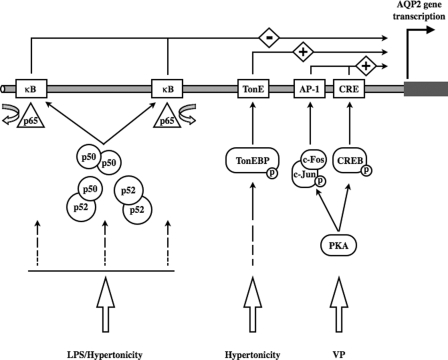
FIGURE 8.
Schematic illustration of controlled AQP2 transcription in collecting duct principal cells. By binding to cis elements of the AQP2 promoter cAMP CREB and AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun) enhance AQP2 transcriptional activity in response to protein kinase A-mediated vasopressin (VP) stimulation. By binding to the TonE element(s) of the AQP2 promoter, TonEBP positively regulates AQP2 transcription under both base-line conditions and in response to hypertonicity. Positive AQP2 transcriptional regulation mediated by both CREB/AP-1 and TonEBP is repressed after activation of the NF-κB pathway in response to either LPS stimulation, characteristic of inflammatory diseases, or hypertonicity. This event is mediated by p65 release from and increased p50 and p52 binding to κB elements of the AQP2 promoter. Although AQP2 transcriptional activity is maintained at low levels under iso-osmotic conditions in the absence or presence of VP, the repressive effect of NF-κB is superseded by increased TonEBP activity after longer periods of hypertonic stimulation. PKA, protein kinase A.