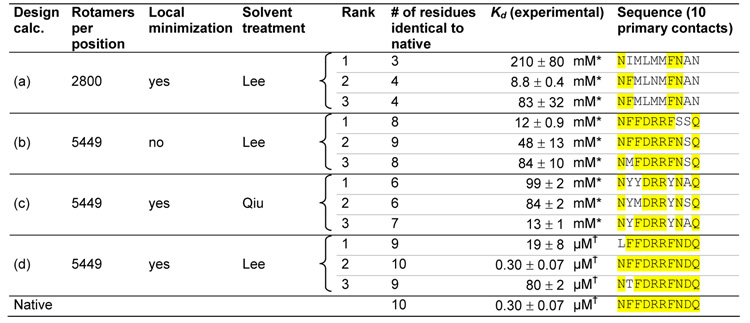
Table 1.
High resolution rotamer library, gradient-based local minimization, and an accurate solvation model are required to successfully redesign the ribose binding site in RBP. Multiple design calculations (a–d) were performed using different sampling resolutions and solvent models. The top three sequences from each calculation and their experimentally measured binding constants are shown. Parts of the sequence identical to the native sequence are highlighted in yellow. (a) Design calculation using a lower resolution rotamer library. (b) Design calculation without a gradient-based local minimization step. (c) Design calculation using a less accurate generalized Born solvent treatment55 (d) Design calculation using a high resolution rotamer library, gradient-based local minimization, and an accurate generalized Born solvation model35 Sequences are ranked by calculated dissociation energy, allowing 5 kcal/mol destabilization relative to the native sequence for 5449 rotamers / position, and 20 kcal/mol destabilization for 2800 rotamers / position. The native sequence was not within the top 100 sequences for design calculations A, B, or C.
 |
Kd measured using the solid phase radioligand binding assay.
Kd measured using the centrifugal concentrator assay. The reported error is the standard deviation of 3 measurements.
