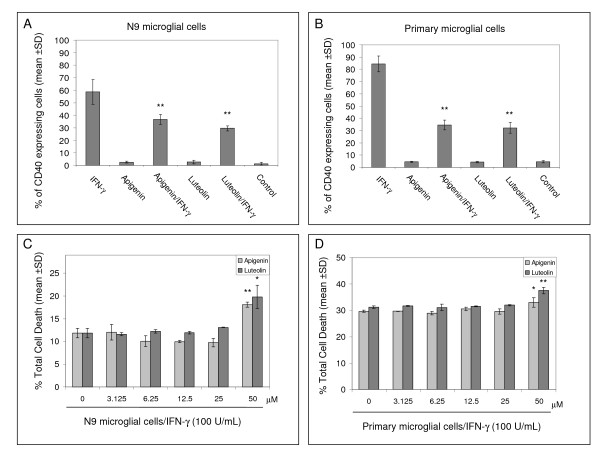
Figure 2.
Apigenin and luteolin inhibit microglial CD40 expression induced by IFN-γ. N9 and murine-derived primary microglial cells were seeded in 6-well tissue-culture plates (5 × 105/well) for FACS analysis and 24-well tissue-culture plates (1 × 105/well) for LDH analysis in parallel. Cultured cells were co-treated with IFN-γ (100 U/mL) in the presence or absence of apigenin and luteolin (25 μM) or treated with vehicle (1% DMSO; control) for 8 hrs. For A and B, FACS analysis showed significant decreases by both apigenin and luteolin (25 μM) in IFN-γ-induced CD40 expression in N9 cells and primary microglia. Data are represented as mean % of CD40 expressing cells (+/- SD). For C and D, cultured supernatants were collected and subjected to LDH assay as indicated. Data showed no significant increase in cell toxicity below a 50 μM concentration of either flavonoid in both N9 or primary microglial cells. Data were represented as mean % of total cell death as determined by LDH present during complete lysis (+/- SD). For A, B, C and D. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).