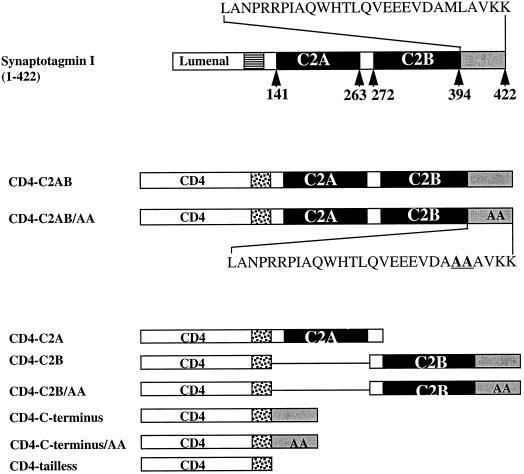
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration showing the CD4-synaptotagmin chimeras. The top line shows the structure of synaptotagmin I, which consists of a lumenal domain (empty box), transmembrane domain (striped box), and cytoplasmic tail comprising C2A, C2B (filled boxes), and the C terminus (gray box). The full amino acid sequence of the C terminus is indicated above. The middle section shows the CD4-synaptotagmin chimeras in which lumenal and transmembrane domains were those from CD4 (empty and dotted boxes, respectively), followed by the entire (wild-type CD4-C2AB) cytoplasmic tail of synaptotagmin I. The position of the di-alanine substitution of Met-Leu within the C terminus is shown in the insert for CD4-C2AB/AA. The lower section illustrates those chimeras in which deletions of the cytoplasmic domain of synaptotagmin have been fused with CD4. CD4-C2A, chimera with truncation both of C2B and the C terminus; CD4-C2B, chimera with a deletion of C2A; CD4-C-terminus, chimera with deletion both of C2A and C2B; CD4-tailless, chimera in which the whole cytoplasmic tail of synaptotagmin has been removed. Positions of di-Ala substitutions within the C terminus are shown within the gray boxes and are reflected in the chimera’s name.