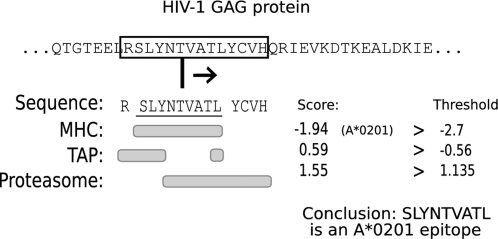
Figure 1. Schematic of the MHC-pathway model.
A window of 14 amino acids is slided across a protein. Each of these ‘14mers’ consists of a N-terminal flanking region of 1 amino acid, a 9mer epitope candidate and a C-terminal flanking region of 4 amino acids. Beneath the 14mer the parts of the peptide that are used by the MHC, TAP or proteasome predictors are marked. Applying the 14mer to the MHC, TAP and proteasome predictors results in three different scores. If each of these scores is higher than a fixed threshold, then the 9mer embedded in the 14mer is predicted to be a CTL epitope for the MHC allele tested (in this case A*0201). If a 14mer passes at least the proteasome and TAP predictors then the 9mer embedded in the 14mer is predicted to be an epitope precursor. In the analysis of longitudinal within-host data sets, CTL epitopes are scored as escapes if mutations in the 14-mer lower one of the three scores below the corresponding threshold.