Figure 1.
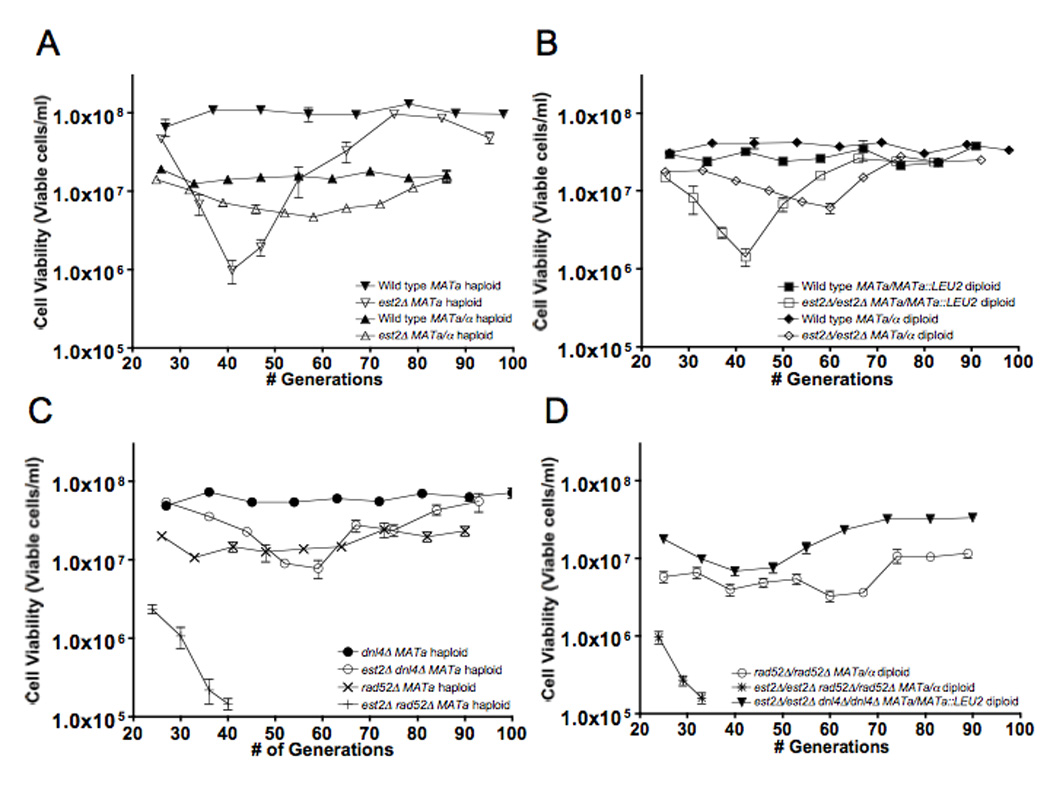
Viability of telomerase deficient cells in serial liquid culture is influenced by NHEJ. Serial liquid growth was performed as described previously (Meyer and Bailis 2007). After each day of serial liquid growth, hemocytometer counts were performed to determine the number of cell bodies, after which 500 cells were plated to YPD medium and incubated at 30° for 3 days. The resulting colonies were counted and the number divided by 500 to determine plating efficiency. Viability was determined by multiplying the number of cell bodies plated by the plating efficiency. Each data point represents the mean viability ±2 SE determined from at least eight independent cultures. The trough of cell viability appearing at 40 or 60 generations corresponds to the point of maximum cell death prior to recovery by HR-dependent telomere recovery. (A) (▲) Wild type MATa/α haploid, (△) est2Δ MATa/α haploid, (▼) Wild type MATa haploid, (▽) est2Δ MATa haploid. (B) (■) Wild type MATa/MATa::LEU2 diploid, (□) est2Δ/est2Δ MATa/MATa::LEU2 diploid, (◆) est2Δ/est2Δ MATa/α diploid, (◇)Wild type MATa/α diploid. (C) (●) dnl4Δ MATa haploid, (○) est2Δ dnl4Δ MATa haploid, (×) rad52Δ MATa haploid, (+) est2Δ rad52Δ MATa haploid. (D) (✱) est2Δ /est2Δ rad52Δ /rad52Δ MATa/α diploid, (○) rad52Δ /rad52Δ MATa/α diploid, (▼) est2Δ/est2Δ dnl4Δ/dnl4Δ MATa/MATa::LEU2 diploid.
