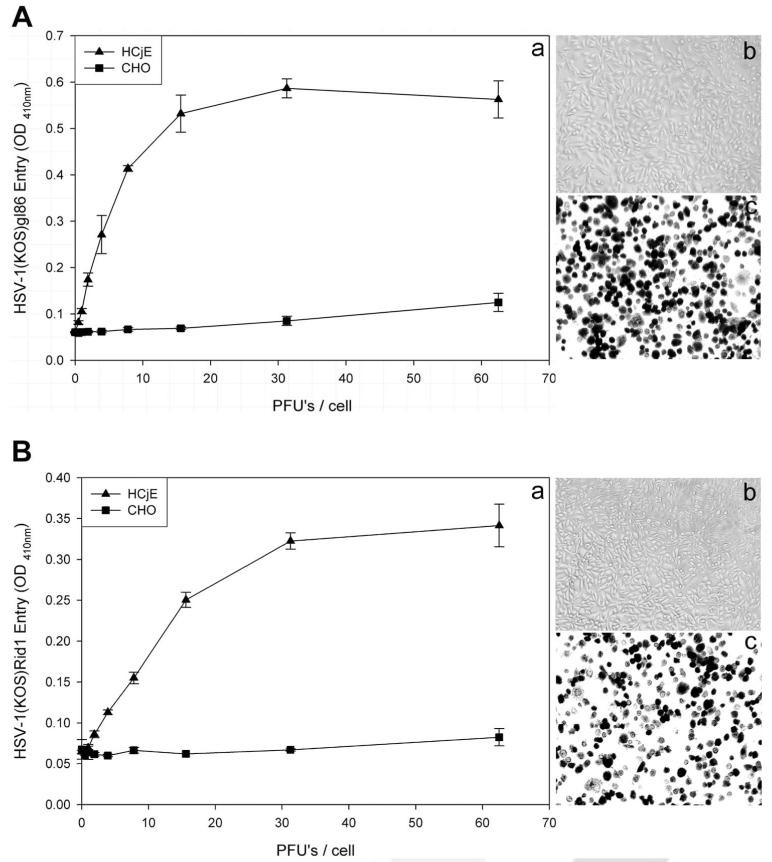
FIGURE 2.
Wild-type and a mutant form of HSV-1(KOS) can enter into HCjE cells. (A) Analysis of wild-type HSV-1 entry into HCjE cells. HCjE or control CHO-K1 cells were plated in 96-well culture dishes and inoculated by serial dilutions of β-galactosidase– expressing recombinant HSV-1(KOS) gL86 virus at the plaque-forming unit (PFU)/cell indicated (a). The soluble substrate, ONPG, was added to cells at 6 hours after infection, and the enzymatic activity was measured with a spectrophotometer (a). Similar as-says were repeated with CHO-K1 (b) and HCjE (c) using an insoluble substrate, X-gal, to monitor individual cells turning blue because of virus entry (shown in black). (B) Analysis of HSV-1(KOS) rid1 mutant entry into HCjE cells. HCjE or the control CHO-K1 cells were plated in 96-well culture dishes and inoculated by serial dilutions of β-galactosidase–expressing recombinant HSV-1(KOS)Rid1tk12 virus at the PFU/cell indicated. ONPG (a) and X-gal (b, c) entry assays were repeated, as described.