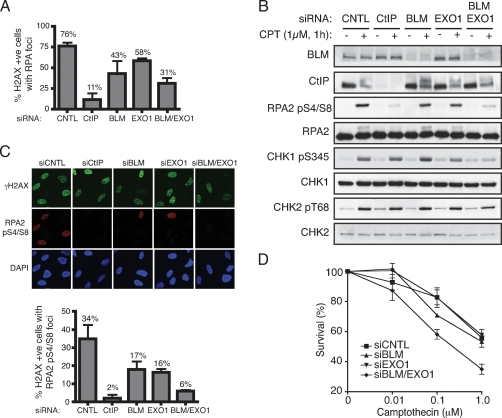
Figure 4.
BLM and EXO1 promote DNA DSB resection and associated events in human cells. (A) BLM and EXO1 deficiency impairs Camptothecin-induced RPA focus formation. U2OS cells were transfected with siRNAs directed against Luciferase (siCNTL), CtIP, BLM, EXO1, or a combination of BLM and EXO1, then 72 h later were mock-treated or treated with 1 μM Camptothecin for 1 h. Cells were next detergent-extracted and fixed, then foci for phosphorylated histone H2AX (γH2AX) and RPA2 were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence. More than 100 cells were counted for each sample and the percentages of cells exhibiting both γH2AX and RPA foci was determined. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. All counting was done blind. (B) BLM and EXO1 promote DSB signaling. Extracts of mock-treated or Camptothecin-treated cells depleted for the indicated factors were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Endogenous EXO1 levels were too low to allow detection with anti-EXO1 antisera and so verification of EXO1 siRNA depletion was done with cells stably expressing a GFP-Exo1 construct (see Supplemental Fig. S4). (C) RPA Ser-4 and Ser-8 phosphorylation (RPApS4/S8) is compromised by BLM and EXO1 depletion. CtIP, BLM, or EXO1 were depleted and cells were treated as in A, followed by analysis by indirect immunofluorescence with the indicated antibodies. More than 100 cells were counted for each sample, and data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Counting was done blind. (D) Codepletion or BLM and EXO1 yields Camptothecin hypersensitivity. Seventy-two hours following transfection with the indicated siRNAs, U2OS cells were treated with Camptothecin for 1 h, and cell survival was determined by colony formation. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.