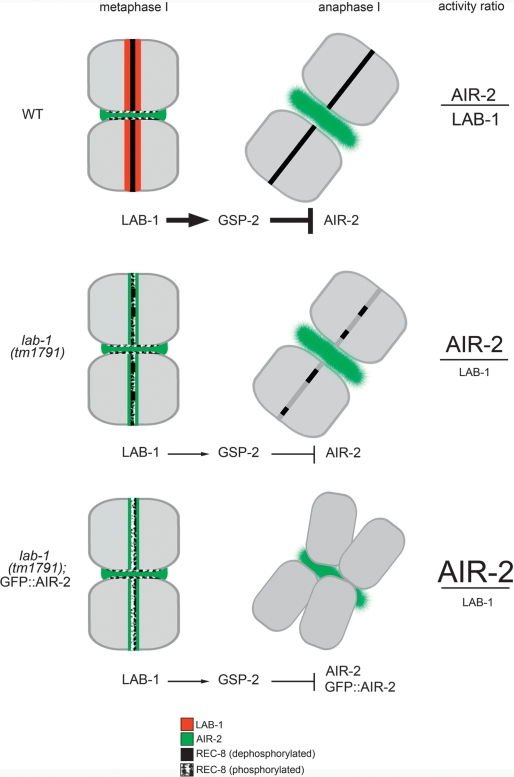
Figure 8.
A model for LAB-1-mediated protection of sister chromatid cohesion. LAB-1 participates in the protection of cohesin by specifically counteracting AIR-2 activity on the long arm domains of the bivalent. This presumably involves the facilitation of GSP-2 activity in this domain. LAB-1 could serve as docking sites for GSP-2, actively recruiting the phosphatase in a shugoshin-like role or it could directly participate in dephosphorylating REC-8. Defects observed due to a decrease in LAB-1 activity, such as premature sister chromatid separation, are proportional to increased doses of AIR-2-mediated phosphorylation. Progressively harsher phenotypes are thus observed when worms carrying a reduced-loss-of-function allele of lab-1(tm1791) are further exposed to ectopic AIR-2 activity from a transgene (GFP∷AIR-2).