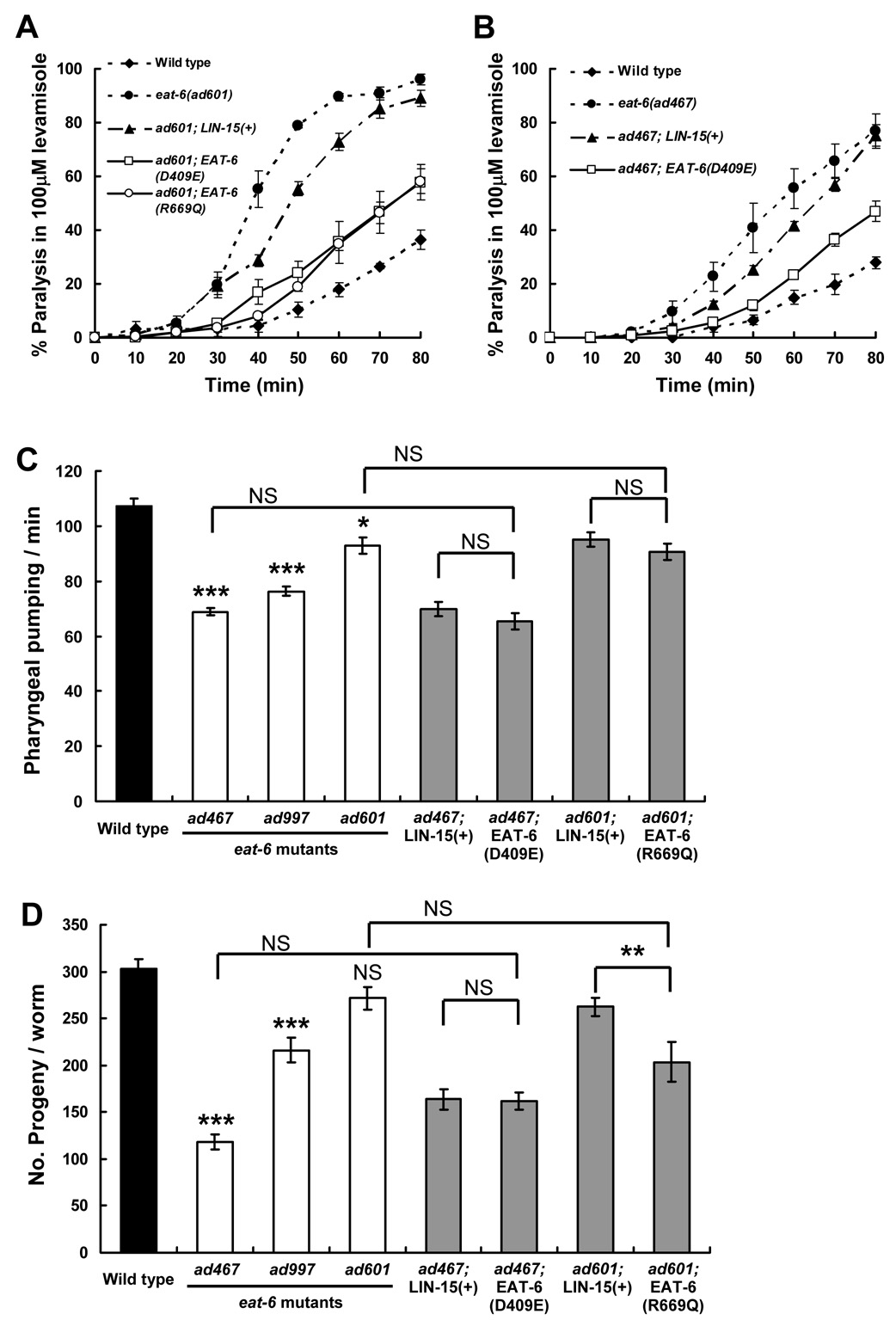
Figure 2. Pump activity-dead EAT-6 mutations recover levamisole sensitivity in eat-6 mutants.
(A, B) Responses to 100µM levamisole in the transgenic animals bearing pump-dead EAT-6 transgenes. LIN-15(+) indicates the control transgene containing only the injection marker DNA. Both D409E and R669Q EAT-6 mutations significantly rescued the increased sensitivity of the ad601 (A) and ad467 alleles (B) (P < 0.05 from 50 to 80 min observation, compared to the control transgenic lines, Student’s two-tailed t-test). Error bars indicate SEM. (C) Number of pharyngeal pumping in 30 s. (n = 12). (D) Average number of progeny per worm. (n = 15). Three eat-6 mutant alleles (white bars) were compared to the wild type (black bar); the results of the statistical analyses are indicated above each bar. Transgenic animals (grey bars) bearing pump-dead EAT-6 were compared to both the corresponding mutant and control transgenic animals. *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05, Student’s two-tailed t-test. NS, not significant. Error bars indicate SEM.